Technology and Industry: RSNA 2006 review: Part 2
The January 2007 issue of Applied Radiology included Part 1 of the review of products displayed at the 92nd Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA 2006), held November 26 through December 1, 2006 at McCormick Place in Chicago, IL. In Part 2 of the coverage, we present more of the innovative technology showcased at this meeting.
GE Healthcare
GE Healthcare (Waukesha, WI) displayed the company's full line of radiology products at RSNA 2006, with particular highlights in the areas of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
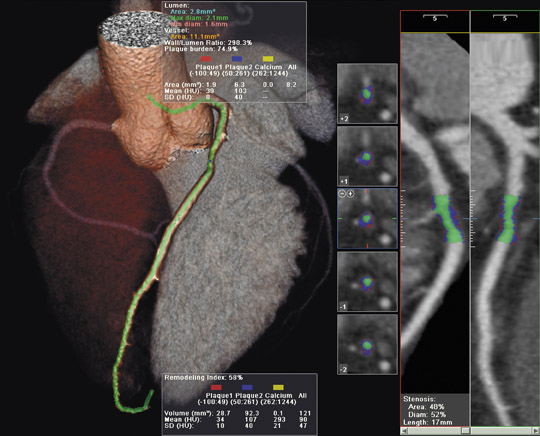
In its CT line, the company featured the new LightSpeed VCT XT scanner, which is capable of capturing images of the heart and coronary arteries in as few as 5 heartbeats. The scanner was also designed to reduce radiation dose by up to 70% during diagnostic cardiac examinations using the new SnapShot Pulse feature. This feature drives a process known as prospective triggered gating in which an automated response to a patient's heart rate ensures that the X-ray is only on for portions of the scan, thereby reducing the patient's radiation exposure time.
"Based on more than 100 patients scanned with our new system, we were able to obtain high image quality for a wide range of patient sizes while the average radiation dose was approximately 5 mSv with a range of 1 to 9 mSv," said Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, MD, head of CT Cardiac Imaging Radiology at the Centre Cardiologique de Nord, Saint-Denis, France.
The system also includes the company's new VolumeShuttle technology. This feature doubles the coverage of the width of the anatomy without increasing the radiation dose (as compared with a single axial acquisition) and uses a single contrast injection. This capability was developed to address the need for wide coverage for both dynamic angiography and perfusion in a single scan for whole-organ anatomic and physiologic assessment.
In addition, GE introduced the latest addition to their BrightSpeed line of smaller, multidetector CT scanners, the BrightSpeed Select (Figure 1). Available in 4-, 8-, and 16-slice configurations, the company notes that the BrightSpeed Select was designed to provide quality images in a smaller scanner system.
"By bringing the innovations of our LightSpeed VCT to the new BrightSpeed Select, we are giving more clinicians access to excellent image quality and, in turn, helping them provide better patient care," said Brian Duchinsky, General Manager of CT Product Development and Marketing.
According to Duchinsky, the BrightSpeed series with the Volara digital data acquisition system offers a high standard of image quality, resolution, and optimal-dose imaging. It also offers productivity tools (such as direct volume visualization with direct multiplanar reformatting) directly on the operator console.
GE also introduced CT analysis software, Perfusion 4 Neuro, for use in the assessment of perfusion, blood volume, and capillary permeability changes that may relate to stroke or tumor angiogenesis. According to the company, this software program "provides quick and reliable assessment of the type and extent of cerebral perfusion disturbances by providing qualitative and quantitative information on various perfusion-related parameters such as regional blood flow, regional blood volume, mean transit time, capillary permeability, and Tissue Classification Index."
The new Tissue Classification Index was developed to assist in determining the status of the tissue based on various perfusion-related parameters during the critical first 6 hours following the onset of symptoms.
"When it comes to the triage of acute stroke patients, 'time is brain,'" said Michael H. Lev, MD, Director of Emergency Neuroradiology and the Neurovascular Lab at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Associated Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA. "The ability to create accurate 'turnkey' perfusion maps with a single mouse click is a welcome and powerful new tool in our stroke diagnostic armamentarium."
In the field of MR, GE featured its Signa High-Density (HD) Head-Neck-Spine MR imaging array. This system allows the user to scan multiple neurology patients or perform a series of examinations on a single patient without changing coils.
The phased-array system features 29 elements and 16 channel outputs to cover a patient's entire upper body with a single coil, providing high-density signals designed to produce uniform high quality images in brain, neck, and spine studies. The modular design allows the user to scan with individual head, neck, or spine sections or to use them together as an integrated unit, while the thoracic and lumbar portion can be left on the table during most examinations.
GE also introduced CartiGram, an MR application designed to assist in the evaluation of articular cartilage integrity. When collagen breaks down, there is increased mobility of water in the cartilage and, consequently, a prolongation in T2 relaxation times. This application, available as an option on the Signa HDx platform, uses T2 values to automatically generate color maps, helping clinicians visualize changes in the composition of articular cartilage.
Philips
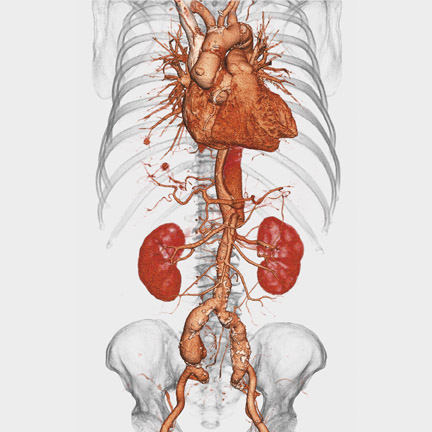
Royal Philips Electronics (Amsterdam, The Netherlands) used RSNA 2006 as the backdrop to showcase its full range of imaging technology and to unveil the company's latest single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system, the Philips BrightView SPECT (Figure 2).
This system, the company notes, "is a fully featured, variable angle camera differentiated by Philips' CloseUp technologies, which enable higher resolution through smarter software, new electronics, and minimal distance between detector and patient."
Designed to accommodate nearly all patients from infants to larger adults, the system features an open gantry and a 450-lb table capacity. It also features the company's BodyGuard technology to move the detectors closer to the patient through automated contouring. The thin imaging pallet and small cardiac dead space were designed to improve image quality in bone and cardiac studies. The compact system also features customizable automated acquisition capabilities to help streamline workflow and allow for future upgrades.
Philips also exhibited the GEMINI TF (time-of-flight) positron-emission tomography (PET)/CT system, which is now available with a 64channel CT component. According to the manufacturer, this system provides enhanced small lesion detectability, shorter scan times, and reduced patient radiation dose. Acquisition of an adult whole-body PET scan with this open-gantry system can be completed in <10 minutes.
The company also announced the availability of a new PET/CT Pulmonary Toolkit that provides respiratory-correlated imaging and intuitive patient feedback on select GEMINI configurations.
In the field of MR imaging, Philips showcased the new Philips Achieva 3.0T X-series, which features enhancements to the magnet, gradient, and radiofrequency (RF) technology and a larger field of view. This system, which will be available in a mobile configuration, features several of the company's imaging and MR application technologies, including spectroscopy, diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS), and SmartExam, which was de-signed to provide one-click planning, scanning, and processing.
Philips also previewed its next generation of computer-aided detection (CAD) software for pulmonary lesions and nodules in digital radiographic chest images. The xLNA Enterprise 2.0, scheduled to be available in the United States in the first quarter of 2007, was designed to assist in the visualization, identification, and evaluation of lung nodules as small as 5 mm.
Summarizing the Philips products displayed at RSNA 2006, CEO Steve Rusckowski said, "Any imaging company can provide clinicians with a lot of data. But at Philips, we strive to intuitively, instantly, and accurately pinpoint the right information to help physicians, nurses, and technologists provide the best possible patient care. Evident from our complete portfolio of healthcare products and technologies introduced this year, Philips consistently develops patient-focused solutions for every stage of care while improving access to systems that enhance the overall quality of care."
IBM
IBM (Armonk, NY) announced at RSNA 2006 that Iowa Health Systems (IHS) plans to use the IBM Grid Medical Archive Solution (GMAS) for its enterprise-wide storage system.
IBM, in conjunction with Bycast Inc. (Vancouver, BC), will help IHS establish a storage system based on the IBM GMAS to manage the healthcare organization's imaging and other fixed content data, such as audio, video, and medical documents. With this system, IBM notes, "IHS will be able to easily deploy a disaster recovery plan over a wide area network, maintain business continuance by allowing clinical applications to operate in the presence of faults, and verify authenticity of retrieved data and auto-rebuild corrupted data."
The GMAS, which is available in single-and multiple-rack configurations, utilizes Bycast StorageGRID software and integrates IBM System Storage DS4000, IBM System Storage EXP100 Expansion Unit, and xSeries servers.
"Customers, such as Iowa Health System, are utilizing innovative technology to help deliver improved patient-centric care," said Bruce Gardner, Director of IBM Healthcare and Life Sciences. "A solution such as IBM GMAS can help reduce the complexity and cost of managing medical images and data so clinicians can effectively and efficiently access patient information."
Ziehm Imaging
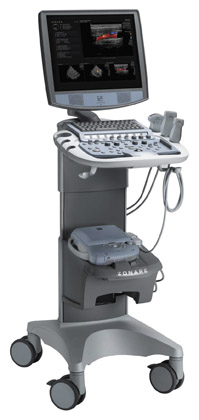
Ziehm Imaging GmbH (Nuremberg, Germany) featured the most recent version of the Ziehm Vario 3D C-arm at RSNA 2006 (Figure 3). This new digital X-ray system features variably isocentric C-arm movement and an interface for intraoperative 3-dimensional (3D) imaging. The user can choose the image intensifier/object distance and, if necessary, may change the settings between the individual exposures without affecting the position of the isocenter in relation to the patient. An on-screen display on the Vario Center interface guides the user through all settings. Following each scan, the 3D image is recomputed and displayed on high-resolution 18-inch flat-screen monitors. A 3D imaging user interface provides optimum orientation within the volume and setting of the diagnostic slices in the coronal, axial, and sagittal planes.
Available options include Active Cooling for unlimited operation time, a generator-mounted laser localizer, a dose area product meter with digital display, and a connector for an external radiation warning light.
The company also introduced its new Object Detected Dose Control (ODDC) tool for the Ziehm Vision series of C-arms. The new tool, which covers the entire field of view, provides real-time motion detection designed to adjust the noise reduction level whenever there are moving objects. The system also reduces the pulse frequency in nonmoving objects. It also features Automatic Metal Correction to reduce the blooming effect when a metal object is in the image.
Kodak
Eastman Kodak Company (Rochester, NY) introduced a new digital radiography (DR) system and a new workstation at RSNA 2006.
The new DR system, known as the KODAK DIRECTVIEW DR 9500, features a ceiling-mounted U-arm, which contains both a tube and detector, that was designed to move around the patient. It provides 2 operator interfaces at the U-arm that allow the technologist to change the X-ray generator parameters and technique settings without leaving the patient. Patient data from a DICOM worklist can also be viewed at the operator interface and at the operator console. The system also features autopositioning capabilities to move the equipment into preprogrammed positions. The KODAK DR 9500 system is scheduled to be available worldwide in the second quarter of 2007.
Kodak also highlighted a new workstation designed specifically for digital image management. According to the company, the Virtual Access Desktop for KODAK CARESTREAM Radiology Solutions is "an entry-level workstation that helps facilitate the transition to a digital environment by equipping technologists, medical staff, and clinical users with basic image review, advanced printing capabilities, and short-term storage." This desktop system features edge enhancement to improve visualization of bone and lung structure, a scrolling feature for long-length CR images, and true-size printing. An optional CD distribution program allows the images to be output to a CD.
"Our digital radiography portfolio illustrates our dedication to innovation and our willingness to develop solutions that meet the divergent requirements and budgets of healthcare providers of all sizes," said Michael L. Marsh, General Manager of Digital Capture Solutions and Vice President, Eastman Kodak Company. "We can deliver a customized solution based on the patient examination applications, room size, volume, and other considerations of each healthcare facility."
Toshiba
Toshiba America Medical Systems, Inc. (Tustin, CA) showcased its new suite of workflow and storage enhancements for its CT systems and previewed, as works-in-progress, the company's new 1.5T and 3T MR systems at RSNA 2006.
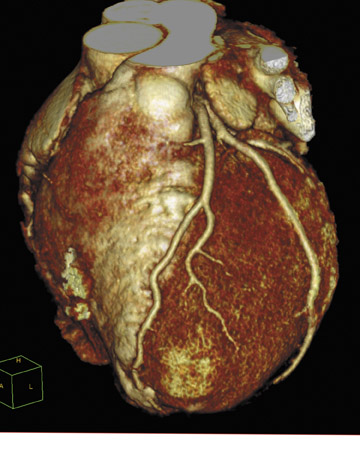
Enhancements to its Aquilion CT system include version 3 software on the CT console, which is designed to provide faster scanning and data analysis. The company also demonstrated the new Automated PhaseXact software component of the SURE Cardio package, which automatically locates the optimal phase of the heartbeat during the image acquisition pro-cess (Figure 4). Version 3 also provides enhanced DICOM data transfers with speeds of up to 60 images per second.
"Toshiba continually strives to raise the standard of care, and we are pleased that clinicians and patients alike will benefit from the industry's highest-performing line of CT systems," said Doug Ryan, Senior Director of CT Business Unit. "These enhancements to our Aquilion systems provide clinicians with the level of confidence they need to optimize diagnosis and enhance overall departmental workflow and efficiency."
Toshiba also announced plans to install the company's first U.S. 256-slice CT scanner, on a beta-test basis, at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and its Heart Institute in February 2007. The system, which will remain at Hopkins for a limited time, will be tested for its usefulness in the early assessment of critical radiology and cardiac CT protocols. This work-in-progress scanner was designed to acquire a volume of data large enough to cover the brain or heart in a single rotation.
In the field of MR imaging, Toshiba previewed its new EXCELART Vantage Atlas 1.5T MR system as a work-in-progress. According to the company, this new 128-element system was designed to "deliver high-resolution images across the entire body with faster imaging times, rendering quick and accurate diagnoses and increasing patient comfort." Its integrated coil was developed to allow clinicians to perform multiple examinations without repositioning the patient. In addition, an optional 205-cm acquisition range allows for feet-first imaging for the entire body, except the neck and head, allowing the patient's head to remain outside the scanner for most studies. Other optional packages include advanced echoplanar imaging, diffusion and perfusion imaging, peripheral angiography and fresh blood imaging, SuperFASE (fast advanced spin-echo) imaging, and Body Vision. The system will also feature the company's SPEEDER parallel imaging technology and its Pianissimo technology for reduced acoustic noise.
Toshiba also previewed a 3T version of the EXCELART Vantage MR system, which features a new magnet design and short-bore combination. This 3T system will include whole-body imaging and spectroscopy designed to capture information not obtainable with 1.5T MR systems.
Compressus
Compressus Inc. (Washington, DC) highlighted its suite of enterprise systems integration software solutions, the MEDxConnect System, at RSNA 2006. Designed to provide connectivity and interoperability between acquisition devices, picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), hospital information systems, radiology information systems, and other related information systems, MEDxConnect components include the Medical Message Mediator (M3), the Virtual Worklist, and the Systems Management Dashboard (SMD).
The M3 component uses communications protocols to control the HIPPA-compliant flow of images, reports, messages, and other data between independent systems. The MEDxConnect Virtual Worklist software runs on the M3 server and enables users to manage diagnostic and reporting workflow by retrieving, routing, and storing all DICOM images and generating worklists from multiple PACS or network systems throughout the enterprise.
The SMD enables the monitoring of enterprise activities and assists in identifying inefficiencies or bottlenecks in workflow, providing a variety of numeric and graphic tools.
"As healthcare enterprises grow in size and complexity, enterprise systems integration will become increasingly vital to the successful management of patient care and the bottom line," said Janine Broda, Vice President and General Manager for Compressus' Medical Solutions Division. "Compressus' MEDxConnect is an innovative technology that supports healthcare's need for a fast, effective, accurate, and affordable solution that provides seamless connectivity and interoperability."
