Pseudomyxoma peritonei secondary to mucocele of the appendix
Images
Pseudomyxoma peritonei secondary to mucocele of the appendix
Findings
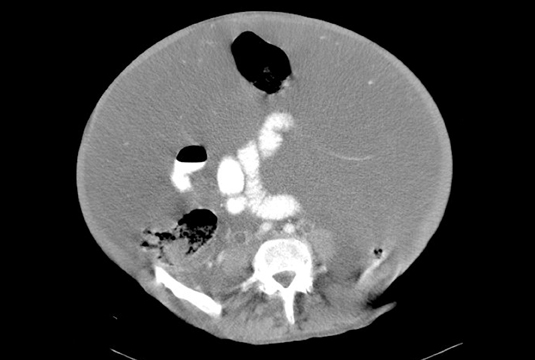
A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis showed a markedly distended abdomen with complex fluid. Additionally, there is a tubular fluid filled structure adjacent to a loop of colon (Figure 1).
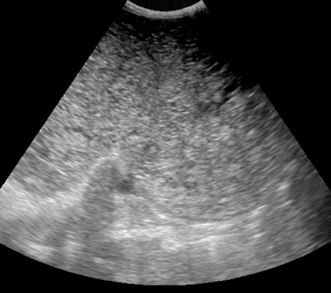
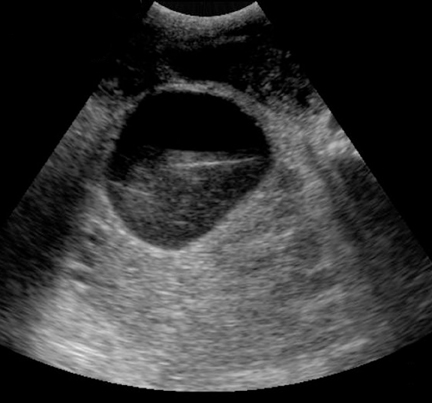
A transabdominal ultrasound reveals a complex mass surrounding the bladder and throughout the lower quadrants consistent with pseudomyxoma peritonei Figures 2 and 3).
Intraoperative findings
Exploratory laparotomy revealed gelatinous-like substance throughout the abdomen and pelvis. Additionally, a tumor in the appendix diagnosed as adenocarcinoma of the appendix.
Discussion
Mucocele of the appendix is defined as a distension of the appendix with mucous occurring in approximately 2% of the population. The etiologies include obstruction by a fecalith or tumor, adhesions, endometriosis or volvulus. Mucinous cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma comprise most of the cases.
The clinical presentation is variable. 50% of cases present with a palpable mass. On ultrasound, the mass can vary in echogenicity from anechoic to hyperechoic. The origin of the mass may be confusing. The differential diagnosis for an appendiceal mucocele in the right lower quadrant includes mesentric duplication cyst, mesenteric cyst, right ovarian cyst, and right hydrosalpinx.
CT can be very helpful in locating and evaluating the extent of disease. Extra-appendiceal spread of disease such as ascites and peritoneal implants are usually signs of malignancy. Pseudomyxoma peritonei is rare, but when present, patients may have abdominal pain with fullness or discomfort. This may result from spillage of mucin causing a foreign body reaction or spread of malignant mucocele. The prognosis for peritoneal disease associated with mucinous adenocarcinoma is poor.
Conclusion
A cystic tumor of the ovary may be mistaken for an appendiceal mucocele and vice versa.
- Zissin R, Gayer G, Kots E, et al. Imaging of Mucocoele of the Appendix with Emphasis on CT Findings. Clin Radiol. 1999;54:826–832.
- Krebs TL, Daly BD, Wong-You-Cheong JJ, Grumbach K. General case of the day: Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the appendix. Radiographics. 1998;18:1049–1050.
- Skaane P, Ruud TE, Haffner J. Ultrasonographic features of mucocele of the appendix. J Clin Ultrasound. 1988;16:584–587.
Related Articles
Citation
Pseudomyxoma peritonei secondary to mucocele of the appendix. Appl Radiol.
August 30, 2011