New Modeling Tools Use Neuroimaging to Investigate Alzheimer Disease Progression
Images
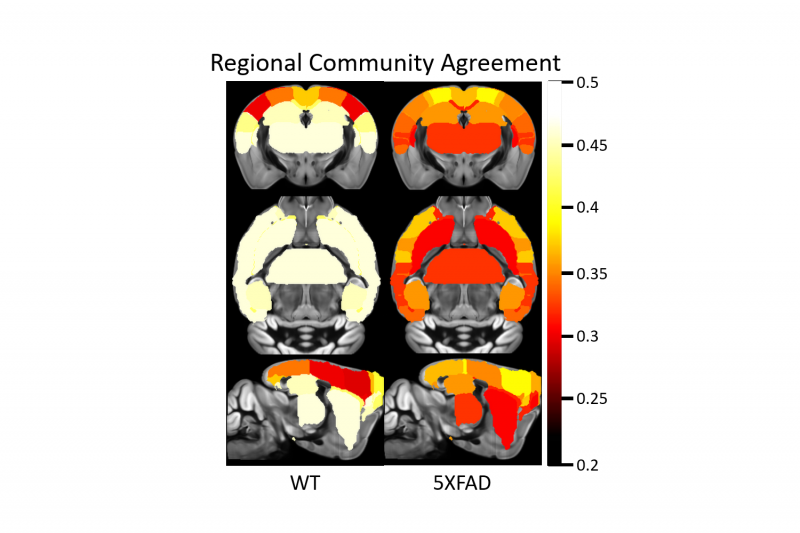
Researchers at Indiana University are using neuroimaging and network modeling tools—previously developed to analyze brains of patients in the clinic—to investigate Alzheimer disease progression in preclinical animal models.
The research team, led by Evgeny Chumin, PhD, a postdoctoral research fellow in the College of Arts and Sciences' Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences at IU Bloomington, and Paul Territo, PhD, professor of medicine at the IU School of Medicine, published their findings in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
More than 6.5 million Americans ages 65 and older are living with Alzheimer disease, and that number could grow to nearly 14 million by 2060, according to the Alzheimer’s Association. While amyloid plaques and tau tangles are the two major hallmarks of Alzheimer disease, research studies also indicate that Alzheimer disease alters glucose metabolism in the brain.
This study looked at metabolic network changes in the brains of Alzheimer disease animal models developed by the Model Organism Development and Evaluation for Late-Onset Alzheimer Disease (MODEL-AD), a consortium of experts at the IU School of Medicine, Jackson Laboratory, University of Pittsburgh and Sage Bionetworks. The tools developed through this research collaboration, Territo said, provide a translational approach to assess disease progression of Alzheimer disease in animal models and bolster the consortium’s rigorous animal model development and preclinical drug testing pipelines developed to study and treat the disease.
“We now for the first time have created tools to assess mouse models carrying human genes, which are built upon the well-established Brain Connectivity Toolbox used in human studies,” Territo said. “We are applying these tools to better understand Alzheimer disease progression and therapeutic response and are embedding them as a resource in MODEL-AD.”
Territo, a primary member of IU School of Medicine’s Stark Neurosciences Research Institute and co-principal investigator of the MODEL-AD consortium, said two past studies inspired his research into analyzing how different areas of the brain interact during disease progression.
Olaf Sporns, PhD, a Distinguished Professor in the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences at IU Bloomington, has previously published papers about network neuroscience, an approach for monitoring disease progression using graph theory and medical imaging—MRI and PET—to map, record, analyze and model the elements and interactions of neurobiological systems in humans. This allows scientists to see changes that occur in the brain’s subnetworks by elevating how neuroimaging like MRI and PET can be analyzed. Chumin is a postdoctoral researcher in the Sporns laboratory.
The other research is from Mattia Veronese, PhD, a scientist from King’s College in London and associate professor at the University of Padua in Italy, who studied human PET imaging data of participants of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) to look for brain network changes and disease progression using the network neuroscience approach developed by Sporns. Veronese is also a co-author on the Alzheimer’s & Dementia journal article.
“Those two pieces of work led our team to develop tools that would extract additional meaning from images of MODEL-AD mouse models, with the goal of not only providing similar whole brain metrics observed in the previous clinical studies, but to also dive deeper and possibly understand how subnetworks within the brain of these models might shed light on the mechanisms of the underlying biology,” Territo said.
Chumin helped develop the tools and resources from the network neuroscience approach of human clinical research to preclinical animal models of MODEL-AD. The investigators analyzed the brain as a whole and also looked at subnetworks within the brain to see how those areas communicate and interact as the disease progresses.
“Using this approach, the research team’s analysis of metabolism changes in animal models confirmed previous clinical findings of disease progression in patients with Alzheimer disease,” Territo said.
The animal models showed age-related changes in glucose uptake as well as differences between males and females—similar to findings from Alzheimer disease human data.
Territo said MODEL-AD plans to use these network neuroscience tools in their investigations of other preclinical data, including models of late-onset Alzheimer disease, potential therapeutics for the disease and multi-modal analyses that combine neuroimaging data from PET and MRI.
Related Articles
Citation
New Modeling Tools Use Neuroimaging to Investigate Alzheimer Disease Progression. Appl Radiol.
December 8, 2023