SponsoredBody ImagingBreast ImagingCardiopulmonary ImagingGastrointestinalNeuro ImagingOncologic Imaging
Clinical Applications in MRI: Managing Patient Outcomes
Images
Introduction
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are indispensable to MR imaging, as they enhance patient care through detailed visualization of tissue and vascular abnormalities.1 GBCAs have faced two areas of concern over the last 20 years.2 The first is nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in patients with severe renal insufficiency, the incidence of which has been near zero in recent years through the implementation of risk mitigation strategies.2 The second is gadolinium retention in body tissues, which, while leading to regulatory actions around the world, still lacks evidence of any clinical consequence.2
The urgent need for a GBCA that reduces unnecessary gadolinium exposure without compromising diagnostic efficacy has driven the development of new options that improve upon the physicochemical properties of older agents. As the most recently approved GBCA, gadopiclenol has captured significant interest because of its high kinetic stability and relaxivity compared with standard GBCAs; these characteristics together allow for administration of a lower gadolinium dose without compromising contrast enhancement.3–7 This article discusses considerations for using gadopiclenol to improve patient care.
The Rationale for Gadopiclenol Use
Balancing the risks and benefits of GBCA administration prior to MRI examination is crucial, particularly for patients who may require repeated examinations over time. These include children, women at high risk for breast cancer who must undergo periodic screening, and patients with chronic conditions that necessitate ongoing monitoring, such as multiple sclerosis.5,8 In all cases, best practices from the American College of Radiology (ACR) dictate the administration of the lowest GBCA dose needed to obtain adequate diagnostic information.2 Therefore, selecting the GBCA that can best answer the clinical question is critical.
Every GBCA contains a gadolinium (Gd3+) ion bound to a ligand that influences the agent’s overall kinetic stability and relaxivity.2 Gadopiclenol was designed to optimize Gd3+ ion access to water molecules, resulting in an r1 relaxivity up to three times higher than that of other GBCAs in water and serum and at all field strengths.3 A high r1 relaxivity is important, as it improves the contrast between abnormal lesions and surrounding tissues, which can aid diagnosis and treatment planning.3 Phase 3 clinical studies have shown that at the approved dose of 0.05 mmol/kg, gadopiclenol offers similar diagnostic performance to a standard GBCA administered at 0.1 mmol/kg while maintaining a strong safety profile.4,5
A key property of GBCAs is kinetic stability, with macrocyclic agents being more stable than linear agents, owing to the former’s cage-like configuration that allows for tighter binding of the Gd3+ ion.9 While all GBCAs are linked to some degree of gadolinium retention, the higher stability of macrocyclic agents results in lower potential for Gd3+ ion dissociation, reducing the risk of NSF development and gadolinium retention in tissues.10 In studies conducted in rat models, gadopiclenol has been associated with lower gadolinium tissue retention compared to linear GBCAs.11,12
Furthermore, at its approved clinical dose of 0.05 mmol/kg, gadopiclenol results in less gadolinium retention than the standard 0.1 mmol/kg dose of gadobutrol, indicating that retention is dose dependent.13 The ability to deliver a lower gadolinium dose without sacrificing diagnostic quality makes gadopiclenol a highly desirable option among GBCAs.2
Compelling Clinical Research
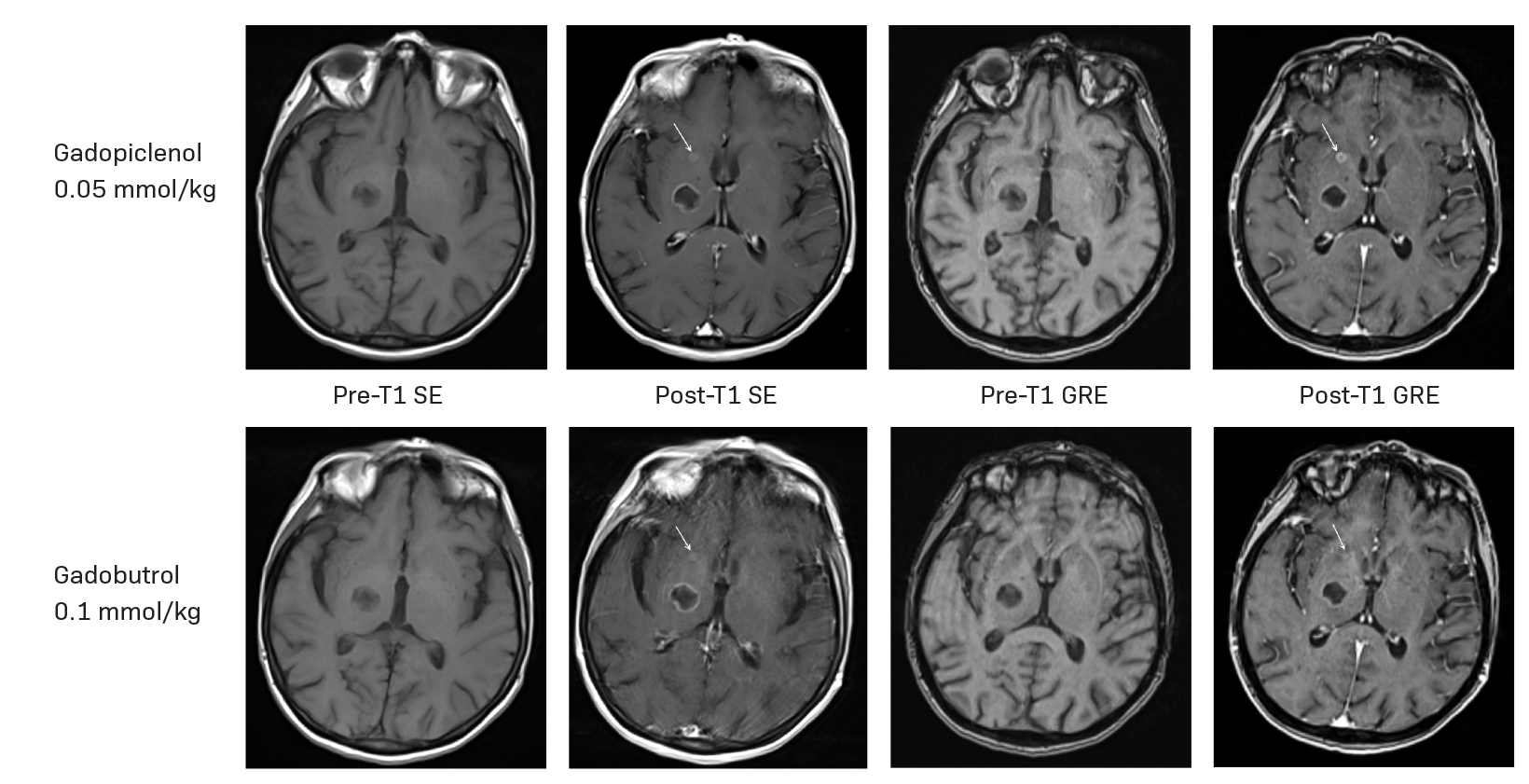
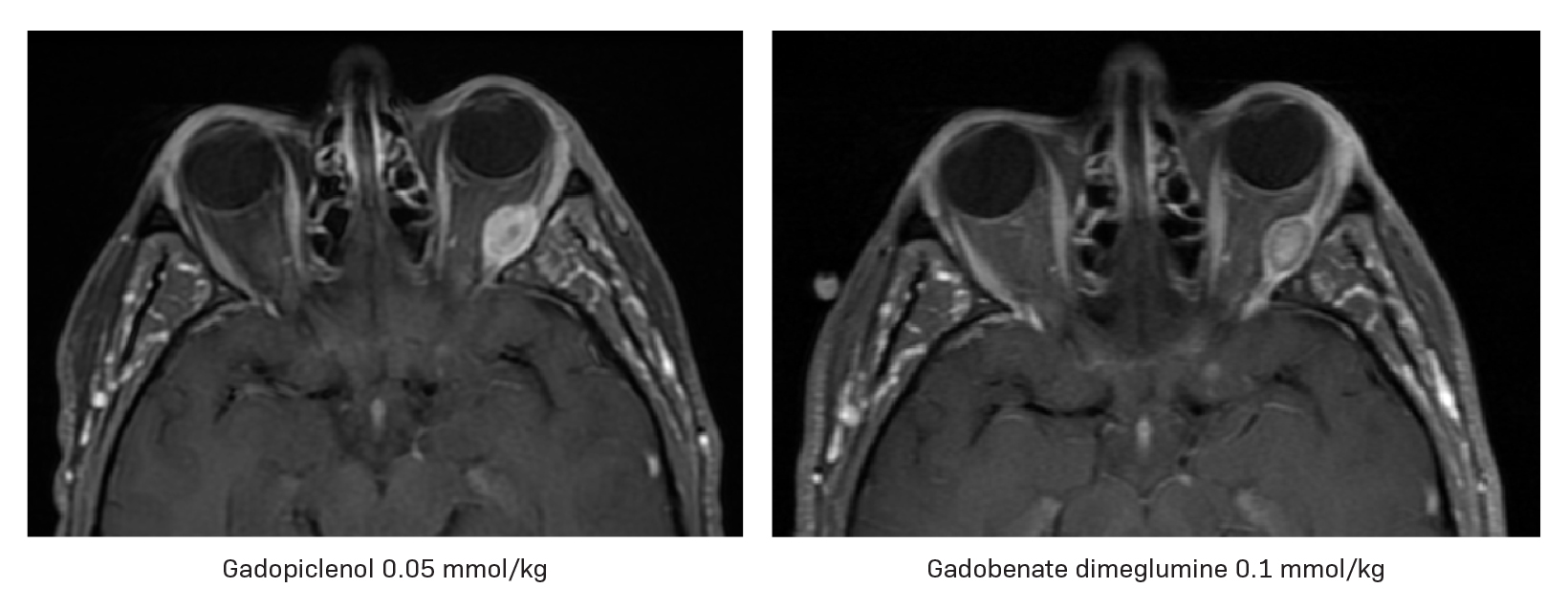
A large body of evidence generated over the past few decades via randomized controlled trials confirms that a high-relaxivity agent can lead to better lesion detection and provide more diagnostic information than a standard-relaxivity agent when administered at the same dose for imaging the central nervous system (CNS).14–18 A similar evaluation was conducted in the phase 3 PICTURE study, which compared a 0.05 mmol/kg dose of gadopiclenol to 0.1 mmol/kg of gadobutrol.4 The primary endpoint, lesion visualization based on border delineation, internal morphology, and contrast enhancement, was assessed by three off-site, blinded readers. A 0.05 mmol/kg dose of gadopiclenol was found to be noninferior to 0.1 mmol/kg of gadobutrol for all evaluated parameters across all readers.4 Gadopiclenol also demonstrated a significantly higher enhancement percentage and lesion-to-background ratio across all readers. Two of the three readers found the contrast-to-noise ratio to be significantly higher with gadopiclenol; they all preferred the gadopiclenol-enhanced images in nearly half of the evaluations.4 The case of a 66-year-old subject with brain metastases from unknown primary cancer enrolled in the PICTURE study is shown in Figure 1.
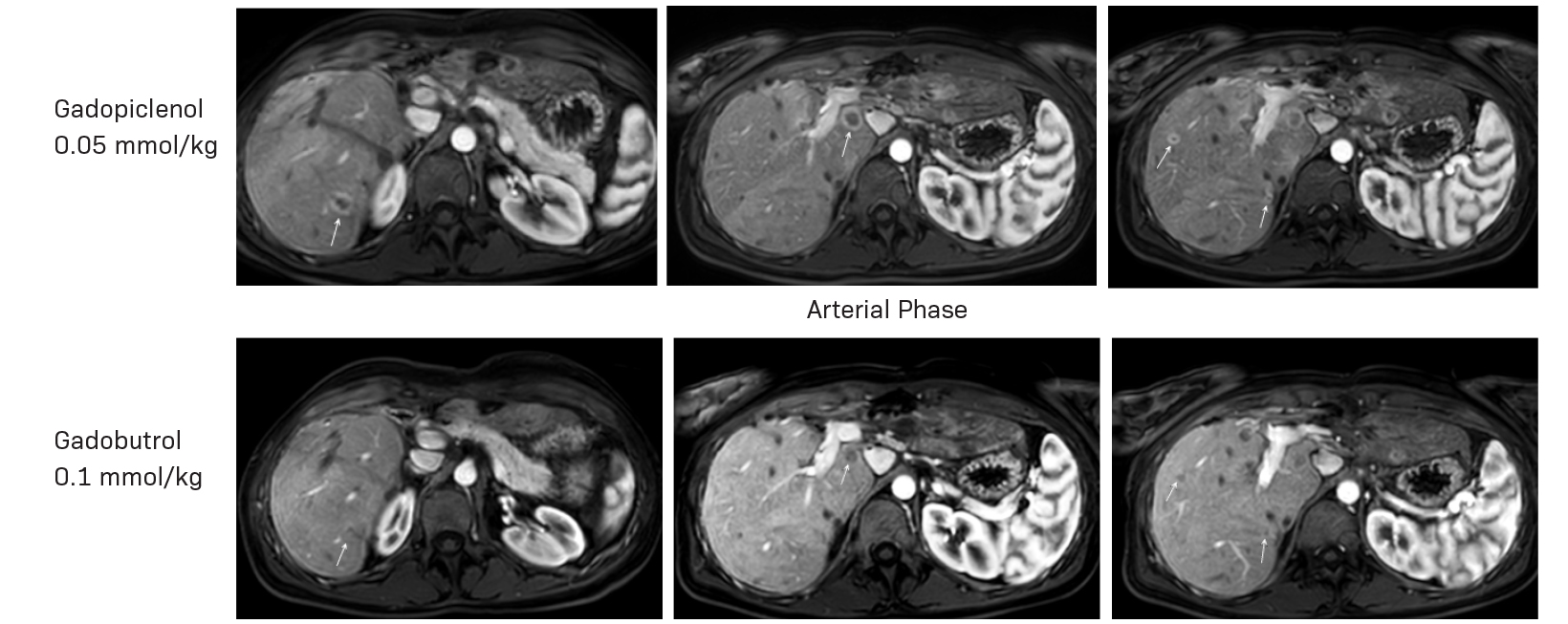
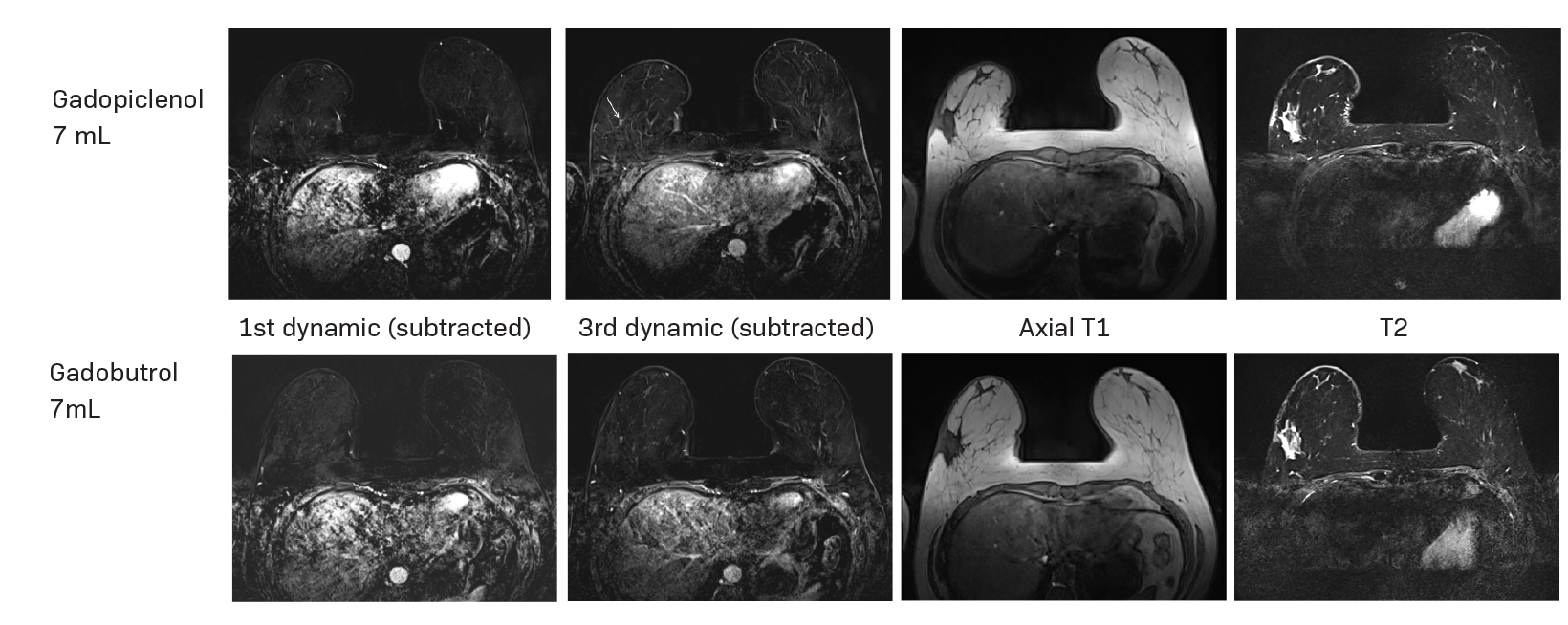
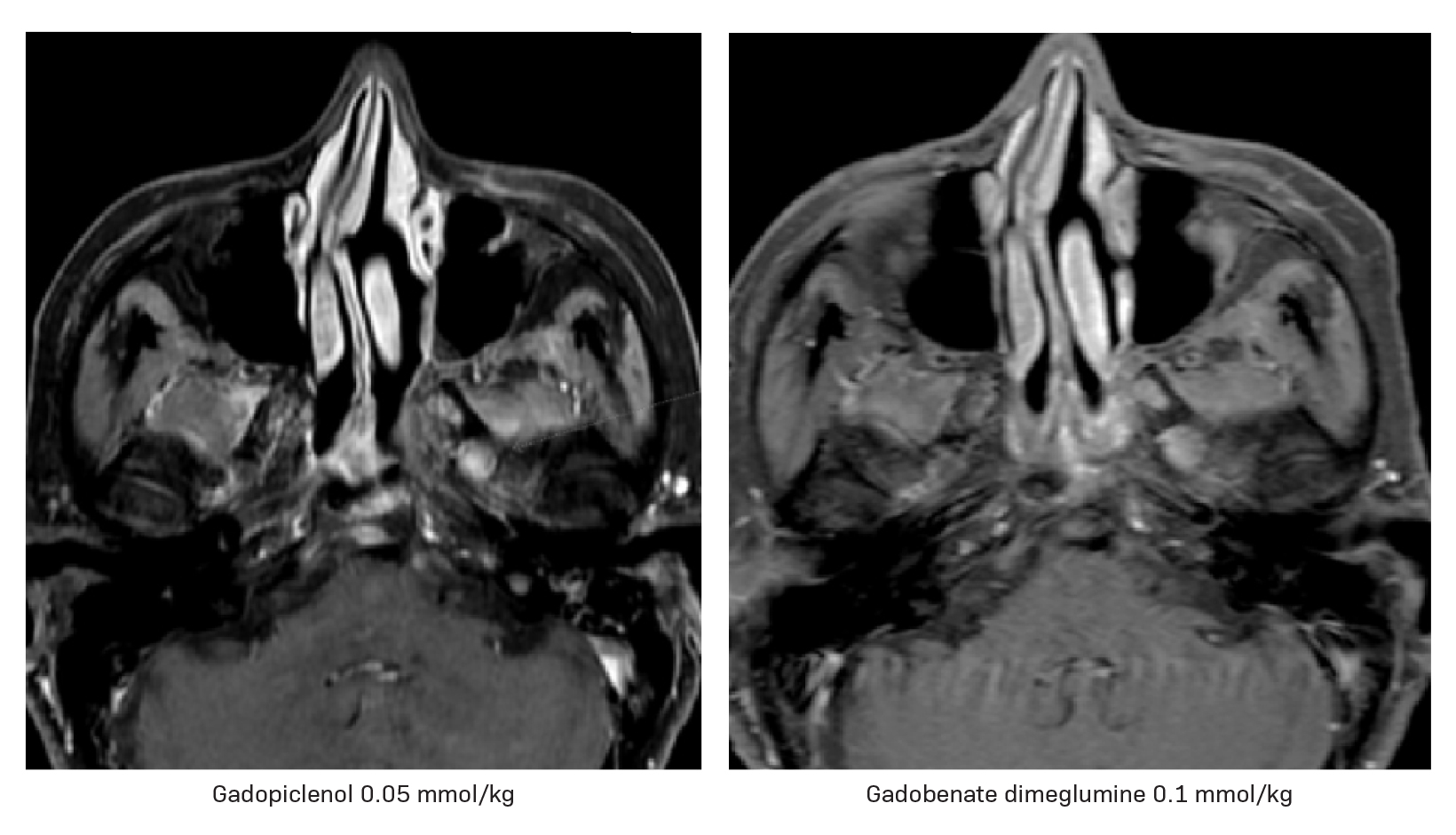
Gadopiclenol has also been studied in contrast-enhanced body MRI. The phase 3 study, PROMISE, found a 0.05 mmol/kg dose of gadopiclenol comparable to 0.1 mmol/kg of gadobutrol in 272 adults with at least one suspected focal lesion in one of three different body regions (head and neck; breast, thorax, abdomen, and pelvis; and the musculoskeletal system).5 Gadopiclenol was shown to be noninferior to gadobutrol for all qualitative visualization parameters and across all readers. Readers also indicated no significant difference in preference between gadopiclenol- and gadobutrol-enhanced images for most patients. Case examples of a 61-year-old male with cholangiocarcinoma (Figure 2) and a 51-year-old female with right breast cancer (Figure 3) show that contrast-enhanced MRI scans obtained with gadopiclenol are similar to those obtained with gadobutrol. In both studies, a half gadolinium dose of gadopiclenol was comparable to a full gadolinium dose with gadobutrol in terms of the degree of contrast enhancement and quality of morphologic lesion characteristics.4,5
Impact of Gadopiclenol on Patient Care
At The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, we see very sick patients who often travel long distances for oncologic imaging and treatment. As we consider the types of patients and their imaging needs, we have found great value in incorporating gadopiclenol into our workflow.
By using an agent that provides twice the r1 relaxivity of standard MRI contrast agents but at half the amount of gadolinium required for optimal imaging, we can improve patient care by detecting small lesions that may not demonstrate significant contrast with the surrounding normal brain tissue or assess their size and number, while minimizing gadolinium exposure (Figures 4 and 5). This is particularly meaningful in vulnerable patient populations such as those who require repeated MRI examinations.
We have also observed another noteworthy benefit with gadopiclenol in patients who require scanning of multiple body regions: same-day imaging. Historically, MRI acquisition limitations associated with standard GBCAs meant that multiple body regions had to be scanned over successive days using multiple doses of GBCAs. For instance, when a patient is referred for an MRI of the abdomen and an MRI of the brain, these two MRI studies would typically be performed on two consecutive days, each of them requiring the injection of a 0.1 mmol/kg dose of a standard GBCA, for a total of 0.2 mmol/kg. However, with gadopiclenol we can perform both scans in one day. In our example, the MRI of the abdomen is performed first with a 0.05 mmol/kg dose of gadopiclenol, after which the patient is quickly repositioned in a head coil to obtain a postcontrast MRI of the brain without reinjecting contrast. This reduces the time to diagnosis and improves overall patient management and workflow. Patients no longer need to travel for multiple visits or extend their stay near our center to accommodate multi-day imaging appointments. The peace of mind that comes from knowing their test results on the same day, moreover, positively impacts our patients’ well-being. There is also an incremental benefit in terms of gadolinium exposure, with only a quarter of the total dose needed for multiple exams with gadopiclenol versus that of a standard GBCA (ie, 0.05 mmol/kg of gadopiclenol vs 0.2 mmol/kg or more of a standard GBCA). This means lower cumulative doses over the course of a patient’s lifetime, especially for those who require long-term follow-up.
Summary
GBCAs improve the diagnostic value of MRI examinations across a wide range of medical conditions. By enhancing tissue contrast for more accurate diagnosis, careful disease monitoring, and improved treatment planning, gadopiclenol represents a critical advance in contrast-enhanced MRI. As highlighted in the case examples discussed in this publication, gadopiclenol has proved invaluable in managing complex conditions such as brain metastases, abdominal pathologies, and many others. While all GBCAs, including gadopiclenol, are not without risk, their benefits in improving patient care are irrefutable. By understanding the behavior and safety profile of gadopiclenol, radiologists can anticipate broad use of the agent to improve diagnostic accuracy and, ultimately, to deliver better patient care.
References
- Kanal E. Gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCA): safety overview after 3 decades of clinical experience. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;34(10):1341-1345.
- American College of Radiology (ACR) Committee on Drugs and Contrast Media. ACR Manual on Contrast Media, 2024. https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/ Files/Clinical-Resources/Contrast_Media.pdf. Accessed July 27, 2024.
- Robic C, Port M, Rousseaux O, et al. Physicochemical and pharmacokinetic profiles of gadopiclenol: a new macrocyclic gadolinium chelate with high T1 relaxivity. Invest Radiol. 2019;54(8):475-484.
- Loevner LA, Kolumban B, Hutóczki G, et al. Efficacy and safety of gadopiclenol for contrast-enhanced MRI of the central nervous system: the PICTURE randomized clinical trial. Invest Radiol. 2023;58(5):307-313.
- Kuhl C, Csőszi T, Piskorski W, Miszalski T, Lee JM, Otto PM. Efficacy and safety of half-dose gadopiclenol versus full-dose gadobutrol for contrast-enhanced body MRI. Radiology. 2023;308(1):e222612.
- VUEWAY® (gadopiclenol) solution for injection, 485.1 mg/mL. Full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide. Bracco Diagnostics Inc. Princeton, NJ; March 2025.
- Elucirem™ (gadopiclenol) injection. Full Prescribing Information. Princeton, NJ: Guerbet LLC.; September 2022.
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns that gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are retained in the body; requires new class warnings. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-fda-warns-gadolinium-based-contrast- agents-gbcas-are-retained-body. Accessed September 15, 2024.
- Idée JM, Port M, Robic C, Medina C, Sabatou M, Corot C. Role of thermodynamic and kinetic parameters in gadolinium chelate stability. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30:1249-1258.
- McDonald RJ, Levine D, Weinreb J, et al. Gadolinium retention: a research roadmap from the 2018 NIH/ACR/RSNA workshop on gadolinium chelates. Radiology. 2018;289(2):517-534.
- Fretellier N, Rasschaert M, Bocanegra J, et al. Safety and gadolinium distribution of the new high-relaxivity gadolinium chelate gadopiclenol in a rat model of severe renal failure. Invest Radiol. 2021;56(12):826-836.
- Funke SKI, Factor C, Rasschaert M, et al. Long-term gadolinium retention in the healthy rat brain: comparison between gadopiclenol, gadobutrol, and gadodiamide. Radiology. 2022;305(1):179-189.
- Rasschaert M, Couloumy E, Renard E, et al. Reduced Gd exposure over 5 months after a single human equivalent dose of gadopiclenol as compared to gadobutrol in healthy rats. Neuroradiology. 2023;65(Suppl):S580 (1-P37).
- Maravilla KR, Maldjian JA, Schmalfuss IM, et al. Contrast enhancement of central nervous system lesions: multicenter intraindividual crossover comparative study of two MR contrast agents. Radiology. 2006;240:389-400.
- Rowley HA, Scialfa G, Gao PY, et al. Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of brain lesions: a large-scale intraindividual crossover comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine versus gadodiamide. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:1684-1691.
- Rumboldt Z, Rowley HA, Steinberg F, et al. Multicenter, double-blind, randomized, intra-individual crossover comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine and gadopentetate dimeglumine in MRI of brain tumors at 3 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29:760-767.
- Seidl Z, Vymazal J, Mechl M, et al. Does higher gadolinium concentration play a role in the morphologic assessment of brain tumors? Results of a multicenter intraindividual crossover comparison of gadobutrol versus gadobenate dimeglumine (the MERIT Study). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:1050-1058.
- Vaneckova M, Herman M, Smith MP, et al. The benefits of high relaxivity for brain tumor imaging: results of a multicenter intraindividual crossover comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine with gadoterate meglumine (The BENEFIT Study). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36(9):1589-1598.
- Bracco Diagnostics Inc. Data on File; Clinical Study Report GDX-44-010.
- Bracco Diagnostics Inc. Data on File; Clinical Study Report GDX-44-011.
VUEWAY® (gadopiclenol) solution for injection
Indications
VUEWAY injection is indicated in adults and children aged 2 years and older for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect and visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in:
- the central nervous system (brain, spine, and associated tissues),
- the body (head and neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and musculoskeletal system).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. VUEWAY is not approved for intrathecal use.
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
- The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
- Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2), or
- Acute kidney injury.
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
- For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended VUEWAY dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration.
Contraindications
VUEWAY injection is contraindicated in patients with history of hypersensitivity reactions to VUEWAY.
Warnings and Precautions
There are risks associated with intrathecal use of GBCAs that can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of VUEWAY have not been established with intrathecal use and VUEWAY is not approved for intrathecal use.
Risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is increased in patients using GBCA agents that have impaired elimination of the drugs, with the highest risk in patients with chronic, severe kidney disease as well as patients with acute kidney injury. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
Hypersensitivity reactions, including serious hypersensitivity reactions, could occur during use or shortly following VUEWAY administration. Assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders, administer VUEWAY only in situations where trained personnel and therapies are promptly available for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, and observe patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions after administration.
Gadolinium retention can be for months or years in several organs after administration. The highest concentrations (nanomoles per gram of tissue) have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (brain, skin, kidney, liver and spleen). Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies, when possible.
Acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs in patients with chronically reduced renal function. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent.
Extravasation and injection site reactions can occur with administration of VUEWAY. Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of VUEWAY.
VUEWAY may impair the visualization of lesions seen on non-contrast MRI. Therefore, caution should be exercised when VUEWAY MRI scans are interpreted without a companion non-contrast MRI scan.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 0.5%) are injection site pain (0.7%), and headache (0.7%).
POST-MARKETING EVENTS
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of GBCAs.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Acute pancreatitis with onset within 48 hours after GBCA administration.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visitwww.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VUEWAY (gadopiclenol) solution for injection including BOXED WARNING on Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis.
Manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by Liebel-Flarsheim Company LLC - Raleigh, NC, USA 27616.
VUEWAY is a registered trademark of Bracco Imaging S.p.A.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
510 Carnegie Center
Suite 300
Princeton, NJ 08540 USA
Phone: 609-514-2200
Toll-Free: 1-800-631-5245 (U.S. only)
Fax: 609-514-2424
©2025 Bracco Diagnostics Inc. All Rights Reserved.
US-VW-2500002 3/25
Citation
M W. Clinical Applications in MRI: Managing Patient Outcomes. Appl Radiol. 2025;(2):.
April 8, 2025