SNMMI ’21: Novel Radiopharmaceutical Tracks Protein Responsible for Cancer Growth
Images
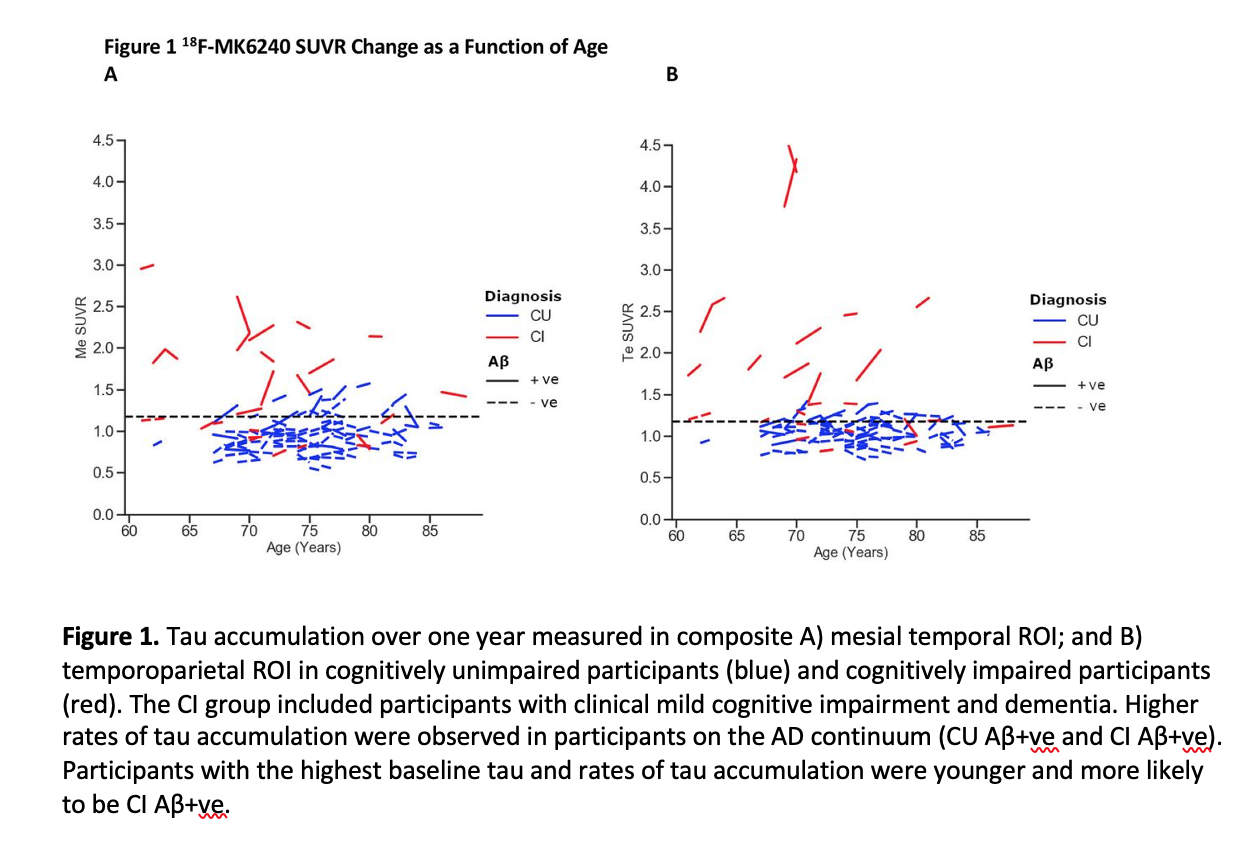
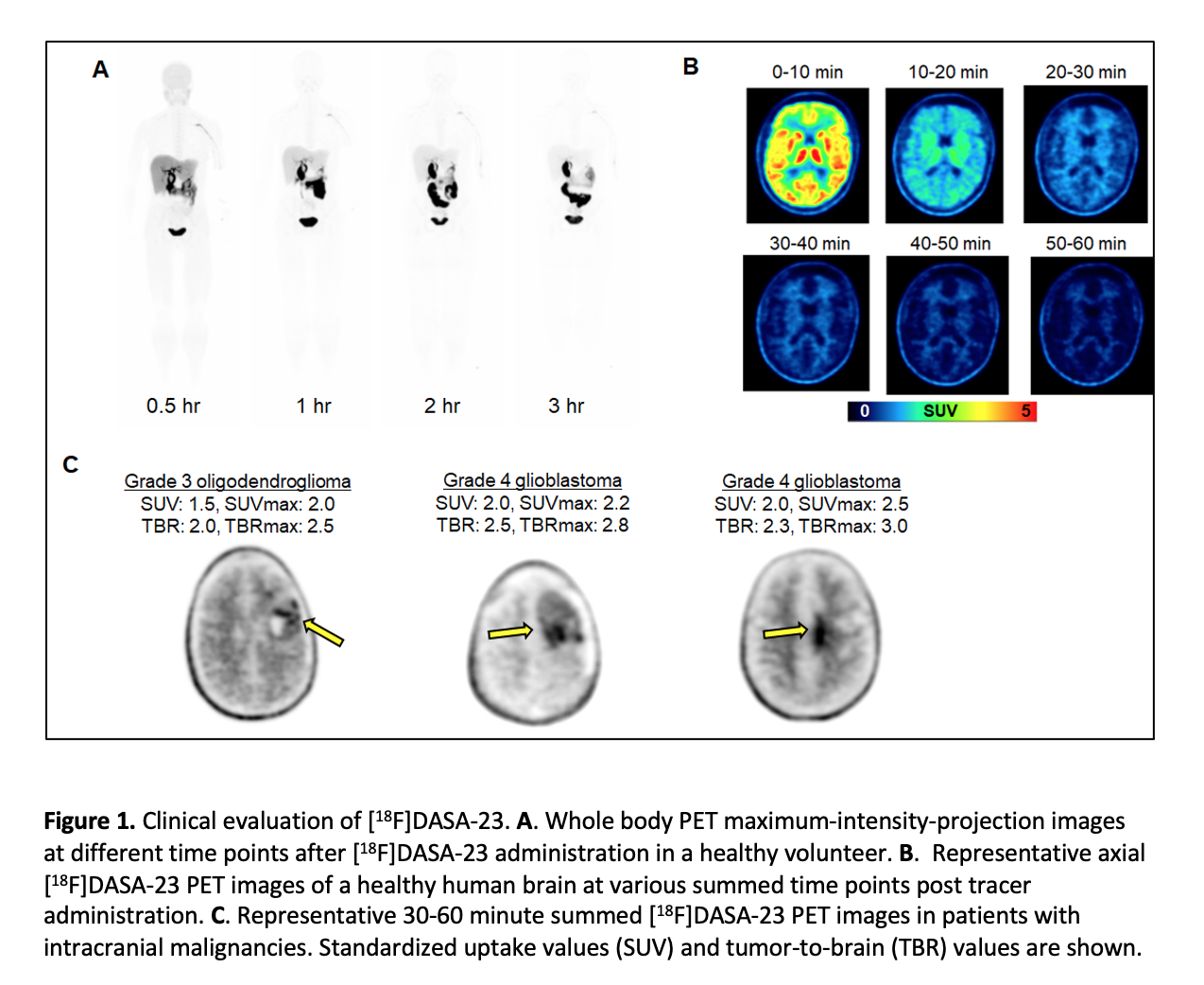 For the first time, a protein critical in cancer cell metabolism has been imaged with the newly developed radiopharmaceutical18F-DASA-23. Imaging with this novel agent has the potential to improve the assessment of treatment response in cancer patients, specifically those with brain tumors. The study was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
For the first time, a protein critical in cancer cell metabolism has been imaged with the newly developed radiopharmaceutical18F-DASA-23. Imaging with this novel agent has the potential to improve the assessment of treatment response in cancer patients, specifically those with brain tumors. The study was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
Tumor cells go through various changes to survive and prosper in the body. One of the key changes they make is modifying a master switch, known as pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), which controls cell metabolism and allows the cell to make more of the building blocks necessary for cell division.
“Until now we’ve had no way to assess the presence or activity levels of the PKM2 protein involved in that switch,” said Corinne Beinat, PhD, instructor of radiology in the Radiology/Molecular Imaging Program at Stanford University in Stanford, California. “Through the development of18F-DASA-23, this is the first time we can noninvasively interrogate the biochemistry of a tumor with respect to this master switch PKM2.”
The study focused on patients with glioblastoma brain tumors, as normal brain cells have very low levels of PKM2. Healthy volunteers and patients with glioblastoma underwent positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging with18F-DASA-23. The radiopharmaceutical was successful in visualizing PKM2 in glioblastoma patients, while it was rapidly cleared from the bodies of healthy volunteers.
“This radiopharmaceutical can be very beneficial in assessing whether brain tumor treatments are working,” stated Beinat. “For example, if a brain tumor is treated with a drug and then imaged with18F-DASA-23, we can potentially know very quickly whether the therapeutic approach is working. If it’s not effective, we won’t have to waste more time waiting to see if the tumor itself is shrinking.”
She added that18F-DASA-23 could also possibly be used in other cancers or to learn more about how normal tissues adjust their metabolism during development or in response to varied environmental conditions.
Related Articles
Citation
. SNMMI ’21: Novel Radiopharmaceutical Tracks Protein Responsible for Cancer Growth . Appl Radiol.
June 15, 2021