Orbray Develops Advanced Diamond-Based Radiation Detector for Medical and High-Radiation Applications
Images
Orbray Co., Ltd. has announced the successful development of a next-generation radiation detector built using its proprietary large-diameter, high-quality single-crystal diamond technology. Leveraging diamond’s remarkable physical properties—including superior radiation tolerance—this innovation marks a significant advancement in radiation detection, particularly for high-exposure environments where traditional detectors often fail.
One of diamond's defining advantages is its composition: with an atomic number of six, carbon closely resembles the makeup of biological tissues. This makes diamond detectors especially suitable for medical uses such as diagnostic imaging and radiation therapy. Orbray’s newly developed detectors deliver accurate measurements across a wide spectrum of radiation types, ranging from low-energy diagnostic X-rays to the high-energy X-rays used in therapeutic applications.
Diamond’s exceptional stability under heat and chemicals, along with its fast signal response, make it a compelling choice for radiation detection. In fact, diamonds have been widely researched in fields such as nuclear engineering, high-energy physics, and medical diagnostics. Historically, studies were limited to rare, natural diamond specimens. However, the advent of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) techniques in the 2000s enabled the production of high-purity synthetic diamonds, vastly improving the performance and accessibility of diamond-based detectors.
Among CVD diamonds, single-crystal varieties have shown the most promise due to their superior sensitivity and detailed spectral performance. In contrast, polycrystalline CVD diamonds—while effective in broadening detection area—generally offer reduced sensitivity and less precise spectroscopic capabilities.
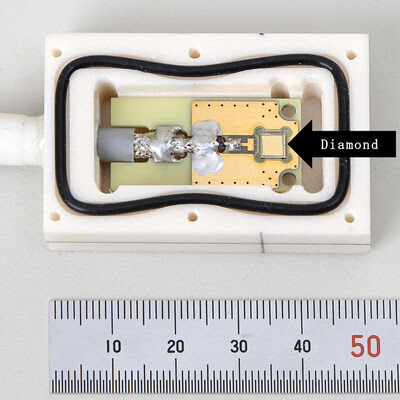
Building on their materials science expertise, Orbray previously achieved a breakthrough in 2021 with the development of a high-quality, 2-inch diameter, free-standing diamond substrate using a proprietary step-flow growth technique. This milestone has now been applied to create high-performance radiation detectors (Fig. 1) in collaboration with academic institutions including Tokyo Metropolitan University, Tohoku University, Tohoku Institute of Technology, and Osaka University.
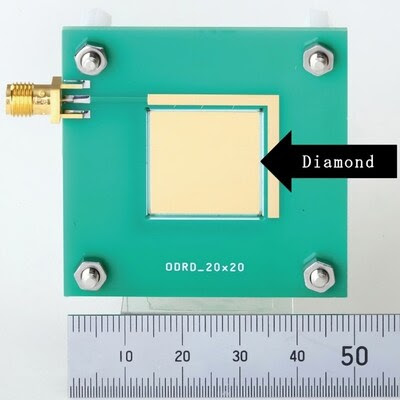
The collaborative effort has led to detectors that demonstrate excellent sensitivity and reliable spectroscopic behavior in medical X-ray systems. Moreover, Orbray has successfully scaled the detectors to a large-area configuration (Fig. 2), which dramatically increases detection sensitivity—opening doors for further applications in precision radiology and research.
Looking ahead, Orbray plans to continue refining these detectors and conducting user evaluations to guide future product development.
The company will showcase its diamond fabrication techniques and present performance data for the new detectors at the upcoming Japan Radiology Congress 2025, taking place in Yokohama from April 10th to 13th. Attendees will also have the opportunity to view the actual detector units on display at the accompanying exhibition.
With this innovation, Orbray is positioning itself at the forefront of diamond-based sensor technology, offering a powerful solution for both medical and industrial radiation detection challenges. By combining robust materials engineering with advanced imaging needs, the company aims to contribute significantly to safer, more accurate diagnostic and therapeutic technologies.