Genicular Artery Embolization for Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis
Images
CME credits are available for this article here.
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the leading causes of chronic disability in adults, affecting more than 9.3 million Americans.1 Many options for managing OA-associated symptoms exist, ranging from conservative therapy to invasive total knee replacement. Conservative treatment includes weight loss, aerobic and muscle-strengthening exercises, NSAIDs, and tramadol.2 Intra-articular steroid injections are an accepted therapy, but hyaluronic acid use remains controversial, as studies have reported no significant benefit compared to other conservative therapies.3,4 Further, intra-articular steroids may accelerate the progression of OA.5
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a well-established treatment for osteoarthritis; however, not every patient is an ideal candidate for TKA, owing to underlying comorbidities.6 Elderly patients with comorbidities, moreover, may be at increased risk of periprosthetic bone fracture. Additionally, the daunting postoperative recovery period serves as a deterrent for patients considering TKA.6,7
Genicular artery embolization (GAE) is a minimally invasive procedure that has shown benefit for managing recurrent hemarthroses post-TKA.8 Recently, GAE has been used to treat medically refractory OA-related pain in patients who are not eligible for or who do not desire to undergo surgery. Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of GAE in controlling pain with an acceptable safety profile.9–16 In this review, we will discuss the pathophysiology of OA, along with procedural details and recent advances regarding GAE.
Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis once was considered a degenerative process from progressive wear and tear of the joint. However, recent research has demonstrated that OA is mediated by an inflammatory cascade and represents a key clinical phenotype of the disease.17,18
When the intraarticular tissues are exposed to excessive or abnormal stress, they generate inflammatory mediators (chemokines and cytokines) and proteases (matrix metalloproteinases), which lead to an inflammatory cascade and alteration of the normal balance between cartilage breakdown and restoration. Chronic bone and synovial inflammation stimulate vascular endothelial cells to form aberrant neovasculature in response to an imbalance between pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors. Pro-angiogenic factors consist of prostaglandin E2, histamine, vascular endothelial growth factor, interleukin-1, platelet-derived growth factor, and nitric oxide.19 In addition, unmyelinated sensory nerves grow around the neovasculature, resulting in pain-related symptoms.20 It is proposed that embolization of the hyperemic knee vasculature curtails this inflammation, inhibiting angiogenesis and proliferation of unmyelinated nerve fibers. Significant reduction in nerve growth factor, a pain and cartilage destruction mediator in OA, have been demonstrated after GAE.21
Animal Models
The synovial changes in OA and the effects of GAE have been evaluated in animal studies. Korchi et al confirmed the presence of synovial inflammation and hypervascularization in knee OA of a canine model using a comprehensive imaging approach and reported a positive correlation of image findings with histopathological analysis. Imaging included conventional MRI, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, contrast-enhanced MRI, and quantitative digital subtraction angiography (Q-DSA). The study also underscored the role of early imaging in diagnosis and monitoring disease progression.22 Ro et al evaluated the efficacy of GAE by randomly assigning rabbit knee OA models to GAE or sham interventions.23 A significant decrease in synovial inflammation and CD3+ cell infiltration was reported among the GAE group, indicating the procedure’s potential to mitigate OA-related symptoms.
Workup and Selection Criteria
Osteoarthritis severity is graded according to the Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) classification model based on radiographic findings such as presence of osteophytes, joint space narrowing and sclerosis.24 Subjective scoring methods for assessing symptom severity include the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis index (WOMAC), the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS), and the visual analog scale (VAS). WOMAC (total score range: 0-96; pain sub-scale score range: 0-20) and KOOS (range: 0-100) involve parameters such as pain, stiffness, physical function, activities of daily living, sport and recreation function, and related quality of life. The VAS considers only one parameter: pain (range: 1-10). Imaging metrics are also sometimes used to quantify symptom severity, known as whole-organ magnetic resonance scoring (WORMS). This approach utilizes conventional MR images and comprises fourteen articular features, focusing on articular cartilage loss and osteophytes, which are recognized as central to OA pathophysiology.25
The GAE selection criteria typically involve patients with radiography-proven, moderate-to-severe OA (within 3 months), who are experiencing moderate to severe pain (VAS > 3), that persists despite conservative treatments (for at least 6 months), and who are ineligible for (or not desiring not to undergo) TKA. Generally accepted contraindications include rheumatoid or other inflammatory arthritis, irreversible coagulopathy, acute knee trauma mandating surgery, prior partial or total knee replacement in the ipsilateral knee, lower-extremity arterial or venous insufficiency, severe iodinated contrast allergy or eGFR < 45. Preprocedural MRI is often performed to rule out other underlying sources of pain and poor treatment response, such as structural abnormalities or malignancy. A thorough history and physical examination are performed and symptom severity is assessed using the subjective scoring methods described above, with majority of the current studies using WOMAC as the scoring tool.26,27
Procedural Technique/Vascular Pruning Technique
Preparation and Setup
GAE is generally performed under moderate sedation on an outpatient basis. Routine prerequisites such as performing basic lab investigations, discontinuing oral anticoagulants, and securing informed consent are completed, and pain sites are identified with radiopaque markers for precision.27
Access and Catheterization
Three approaches can be used to access the femoral artery: Ipsilateral antegrade, contralateral retrograde, and retrograde pedal.28 Access is obtained under local anesthesia and ultrasound guidance, then an angiographic catheter is advanced to the distal superficial femoral artery, a critical step in identifying the genicular branches responsible for the hyperemic regions near the radiopaque markers. Further refinement is achieved by introducing and advancing a microcatheter, often 1.7–2.4-French in size, super-selectively into the genicular arteries for precise targeting. Lower-profile microcatheters (≤ 2 -French) may be considered to enhance navigational ease in complex anatomy.28
Contrast and Embolization
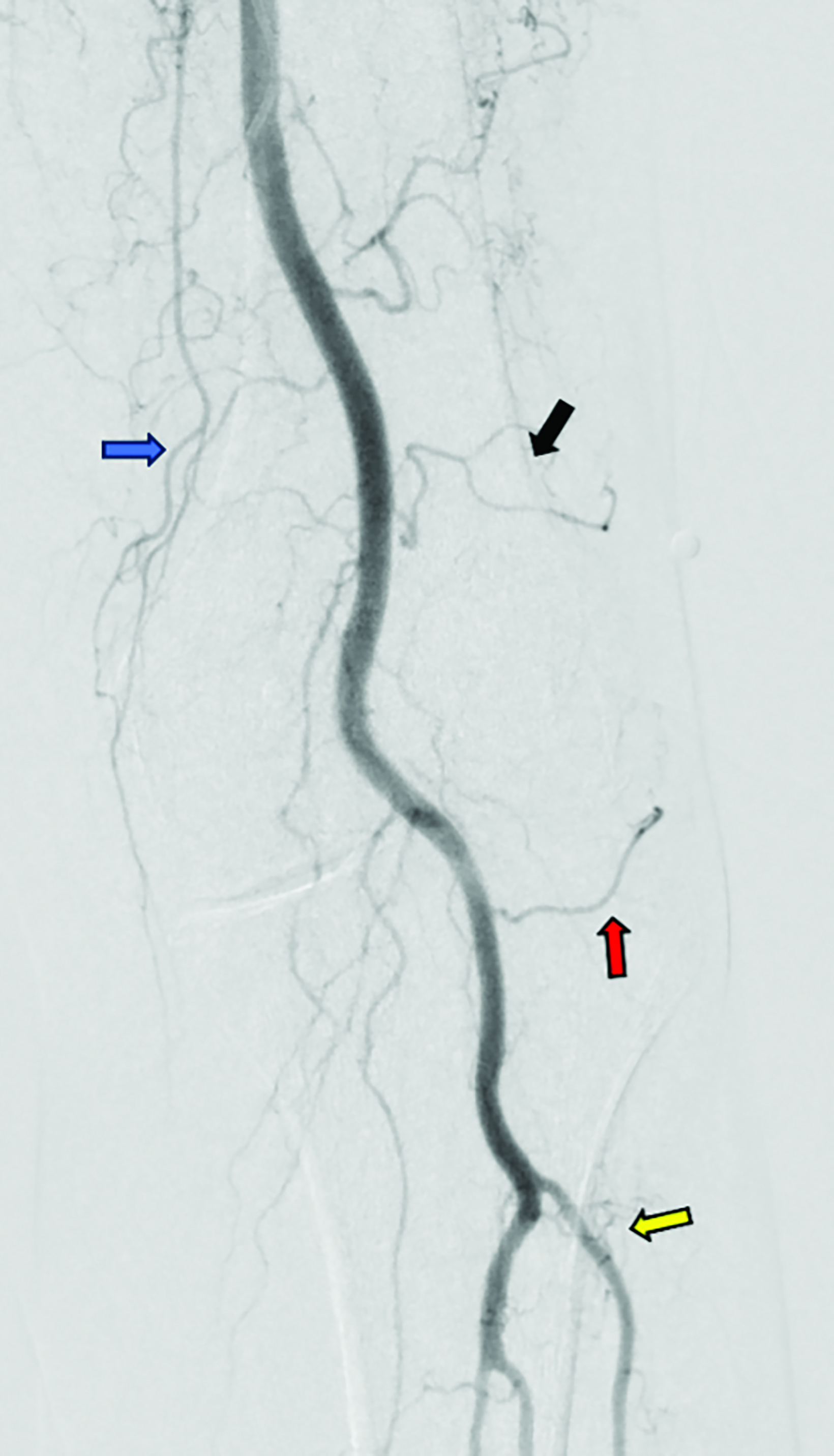
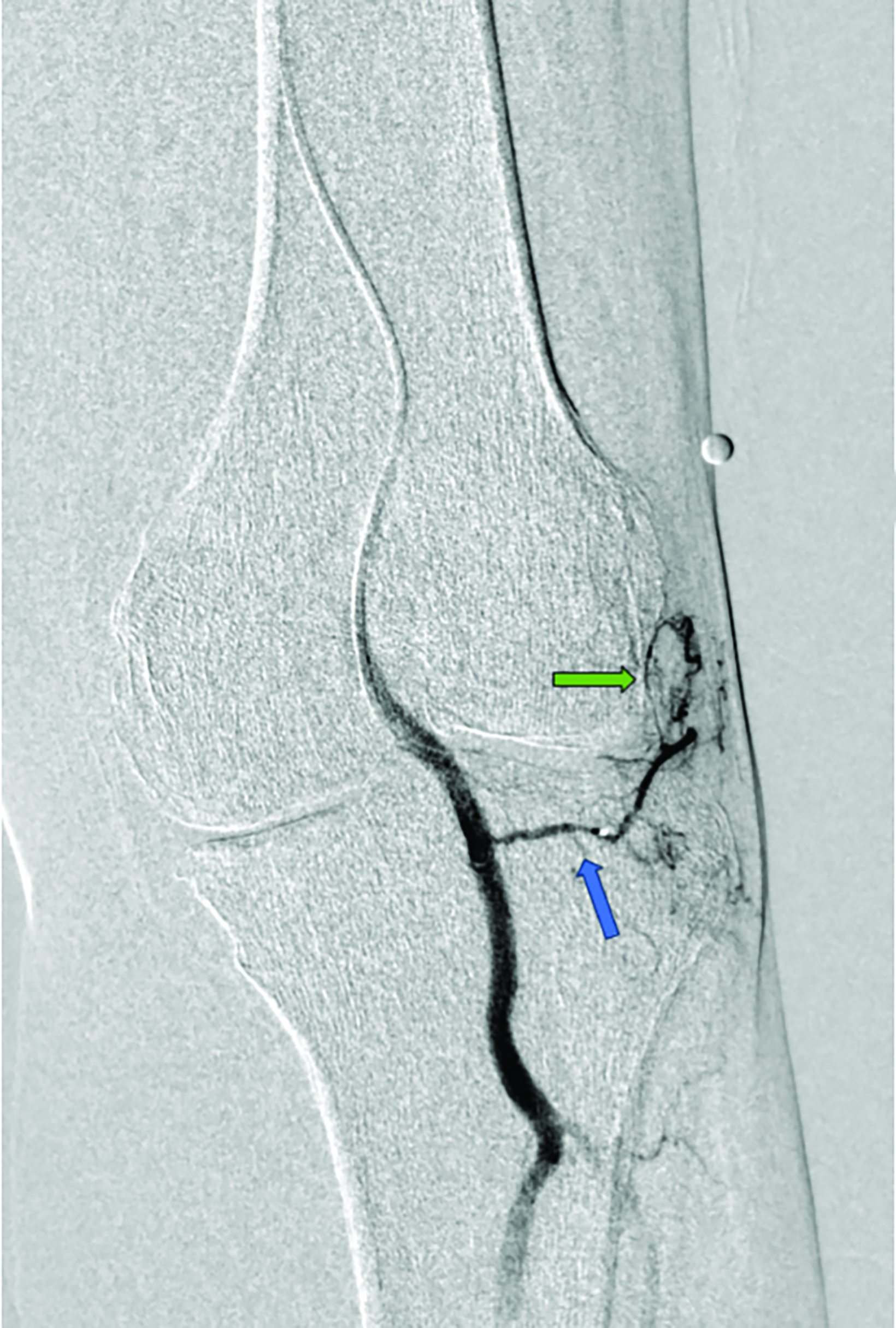
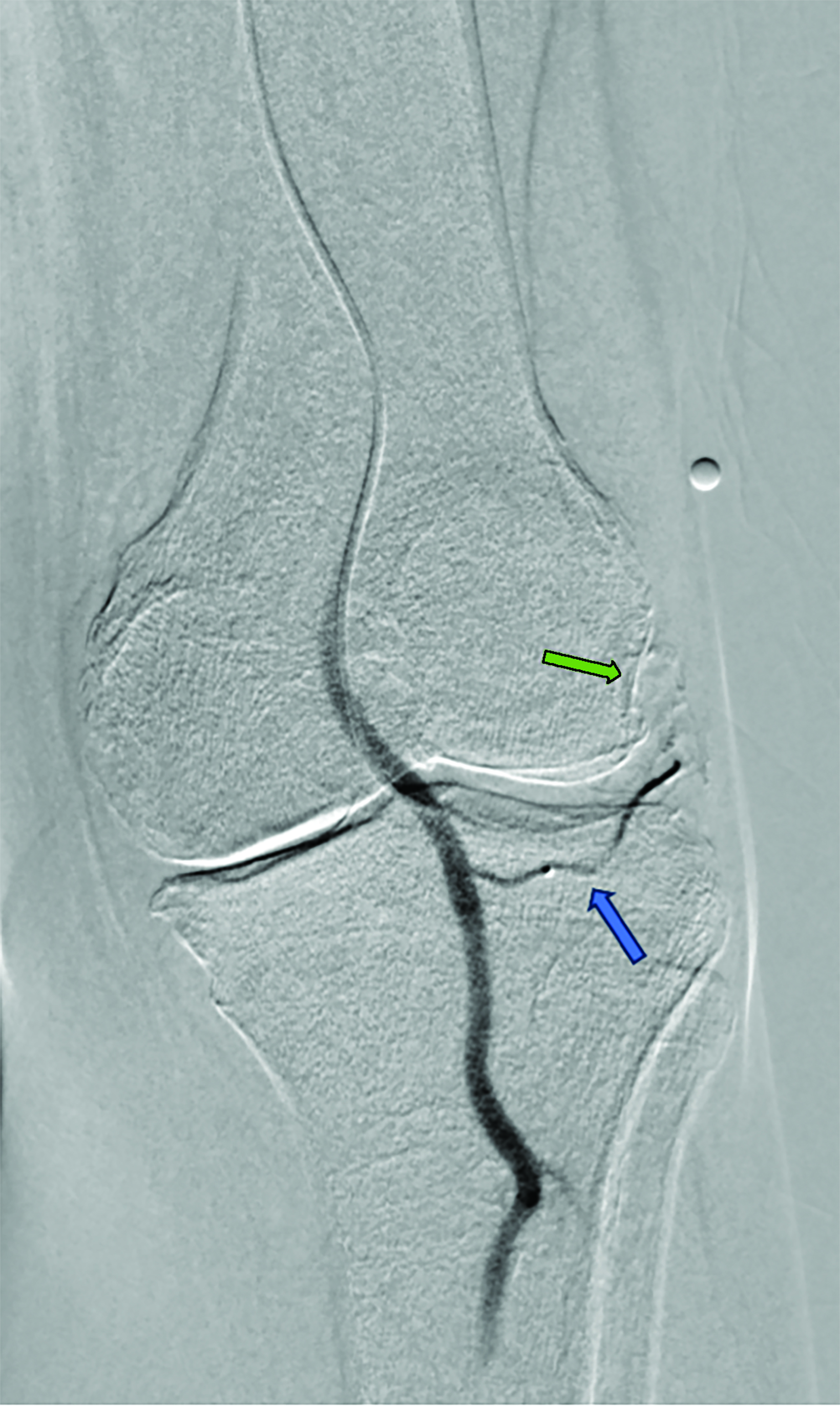
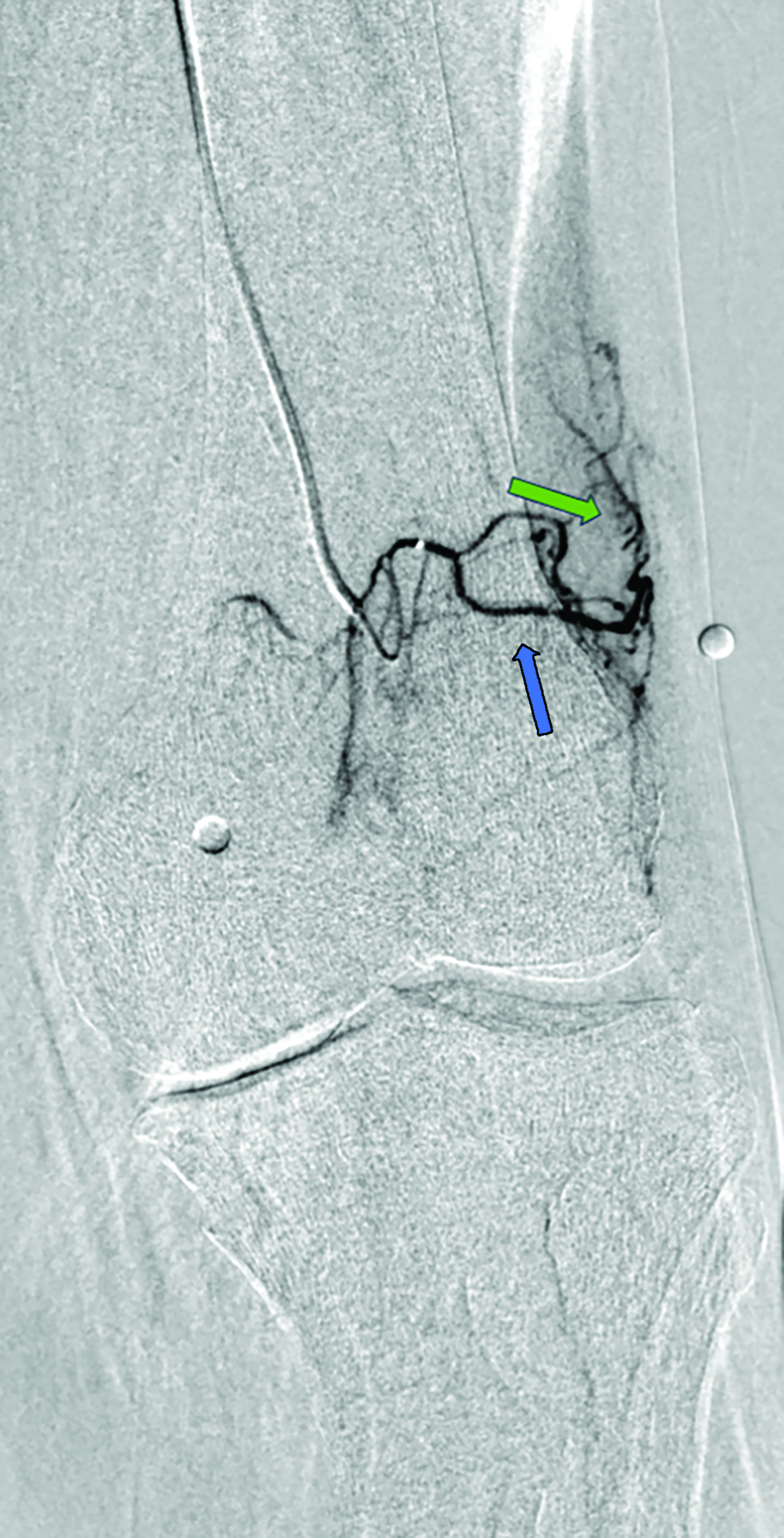
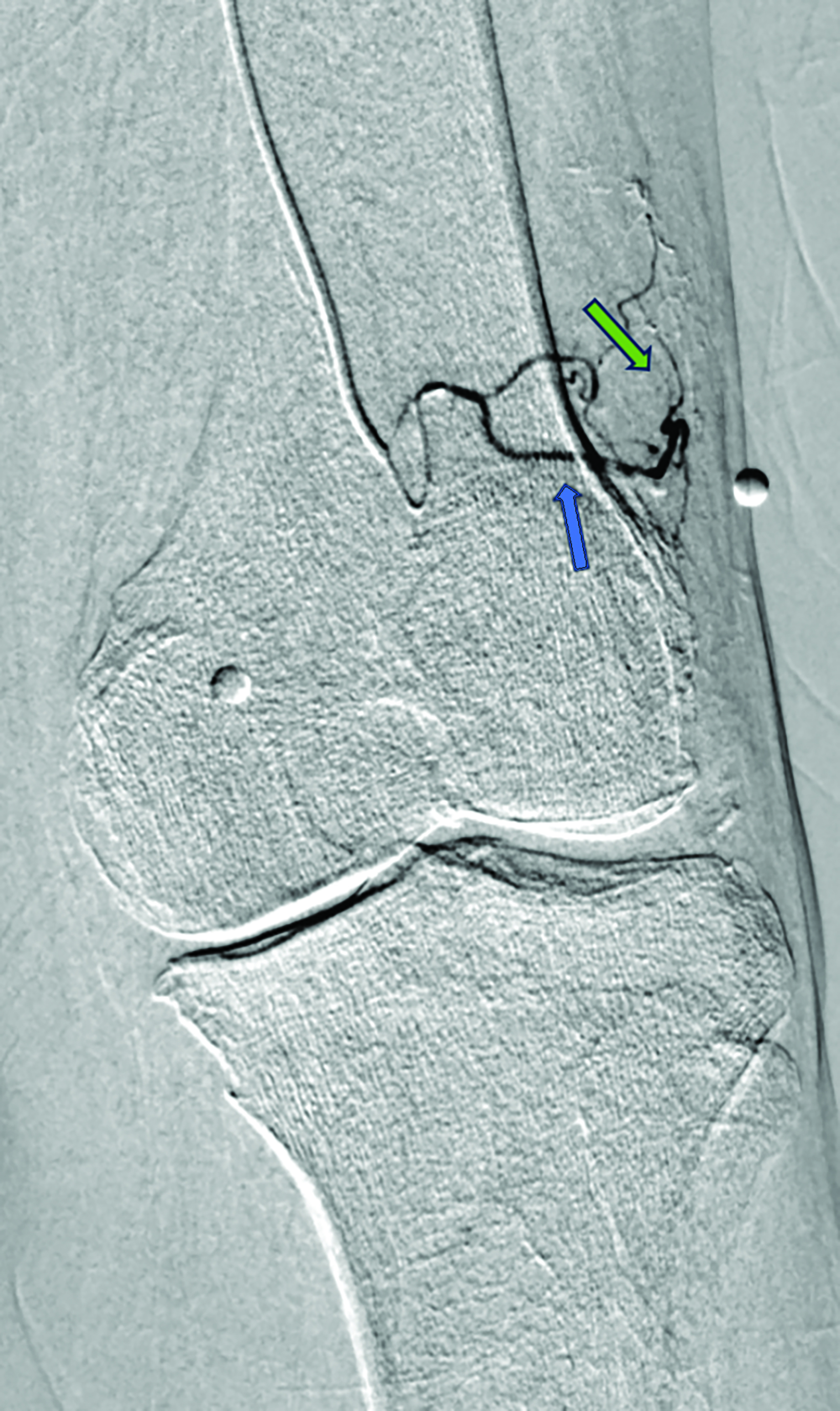
Contrast is administered from the distal superficial femoral artery above the origin of the descending genicular artery. Both early and delayed phase DSA are deployed to facilitate the identification of genicular arteries or any anatomical variants and target hyperemic areas (Figure 1). Additionally, cone-beam CT and angio-CT can be used to map the feeding vessels and to determine vessel obliquity.27 Once the target vessel is reached, the “pruning” method is employed to inject embolic material (miniscule aliquots ranging 0.1-0.4 mL) to achieve sub-stasis.
This technique effectively clears hyperemic vessels while simultaneously ensuring sustained flow within the parent genicular artery and thereby mitigating the risk of ischemic complications.28 This was validated in a pilot study by Badar et al, who reported favorable clinical outcomes and significant perfusion reduction in the target vessels with preserved flow in the parent vessel.29 For enhanced precision, microspheres can be diluted with the appropriate ratio of contrast and saline and injected under fluoroscopic guidance.27,28 The six main target vessels are the descending genicular artery (DGA), the superior medial genicular artery (SMGA), the inferior medial genicular artery (IMGA), the superior lateral genicular artery (SLGA), the inferior lateral genicular artery (ILGA), and the anterior tibial (ATRA) artery.10
Assessment, Additional Treatment, and Postprocedure Care
The resolution of distal hypervascularity while keeping the parent genicular artery and its branches patent marks the technical success of the procedure. Patients are advised to remain supine and maintain their access leg straight in the recovery area for four hours. A steroid taper, such as post-procedure methylprednisolone, and 500 mg naproxen twice a day for five days, can be prescribed to manage short-term postprocedure inflammation and pain.27
Follow-up
Clinical success is determined by amelioration of symptoms at 1, 3, 6, and 12-month follow-up and based on the scoring methods. Physical exams are also performed to rule out any potential adverse events. In the majority of cases, patients with mild to moderate OA report significant improvement within 1-3 months, which may last for years.10 For severe OA, studies have reported initial symptom improvement with relapse on long-term.11–13 In cases of persistent symptoms, repeat intervention has been described.12 For patients who remain non-responsive to treatment, TKA remains a viable option.12,14,15
Types of Embolic Agents
The particulate embolics can be categorized into temporary and permanent. Effective temporary embolics encompass imipenem/ cilastatin sodium (IPM/CS).9–11 IPM/CS represents a combination of antibiotic crystals that generate transient embolic effects when blended with a contrast medium, resulting in particle sizes between 10 and 70 μm.30 Permanent embolics ranging in size from 70-300 μm have also been used in certain studies that prove their efficacies. These include Embozene (75-100 μm; Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, CA), Embospheres (100-300 μm; Merit Medical Systems, South Jordan, UT), Optisphere (100-300 μm; Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN), and polyvinyl alcohol (10-70 μm; Contour, Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA).10,11,31,32 More recently, ethiodized oil-based emulsion (ioversol/ethiodized oil) (Optiray/Lipiodol; Guerbet, Villepinte, France) has been evaluated in a prospective study with significant results.33 Still, the choice of ideal embolic remains a matter of debate.
Adverse Events
The most common adverse events (Society of Interventional Radiology class A and B, Cardiovascular, and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe grade 1 and 2) associated with GAE are skin changes, including but not limited to transient erythema, discoloration, and ulceration resulting from non-targeted embolization of cutaneous arteries; puncture site hematoma; paresthesia; and fever. No seri- ous adverse event has been reported.32
A systematic review by Casadaban et al reported transient skin erythema in 11% (21/186) of patients across three included studies. Embozene exhibited a higher rate (63%) and longer duration (1-3 months) compared to IPM/CS (2.5% and 3 weeks, respectively). The plausible reason for this disparity may be the permanent nature of embozene compared to IPM/CS. Puncture site hematoma was reported in 10% (18/186) patients, with resolution within 1-3 weeks.20 Bagla et al reported paresthesia in the great toe and plantar region in two cases, which ultimately resolved within two weeks.13 Lee et al reported a sole instance of fever that subsided within a day, with a prevalence of 0.5% among 186 cases.11 Padia et al reported hematoma formation at the femoral puncture site, which resolved without any sequelae. Skin ulceration was reported in 18% (7/40) of patients and did not require any treatment. Two small, asymptomatic bone infarcts in non-weight bearing areas were identified on a 3-month follow-up MRI. One case of fat necrosis was found in the lower thigh.15
The risk of cutaneous ischemia can be alleviated by applying ice packs to the affected knee skin to induce vasoconstriction before embolization. Padia et al reported a reduction from 18% to 0% by utilizing this technique.15 Furthermore, higher microsphere volumes (≥ 3 mL) in one setting were reported to be associated with increased risk of cutaneous adverse events.29 However, this volume cutoff pertains to a specific embolic type (200 μm Hydropearl microspheres) and dilution method (1:3) which limits generalizability to other embolics. More studies are needed to consolidate this volume threshold.
Anatomical Variants of the Geniculate Arteries
The popliteal artery is the continuation of the superficial femoral artery. At the knee joint level, the popliteal artery gives the DGA that supplies the anterior portion of the knee joint. Below the origin of the DGA are the SLGA and the SMGA, which supply the lateral and medial portions of the knee joint, respectively. More distally, arising from the popliteal artery, are the ILGA and IMGA. Finally, the ATRA, which arises from the anterior tibial artery, is the most inferior artery supplying the knee. Bagla et al proposed a classification system for the arteries of the knee joint by analyzing the angiographic findings from 41 GAE procedures. The following branching patterns were observed: M1 (presence of all three medial branches: DGA, SMGA, IMGA), M2 (presence of two of the three medial branches: either DGA and SMGA, or DGA and IMGA), L1 (presence of all three lateral branches: SLGA, ILGA, ATRA) and L2 (presence of two or three lateral branches: either ATRA and SLGA, or ATRA and ILGA). Understanding these variants is crucial as it may help decrease the risk of non-target embolization and prolonged radiation exposure.
Outcomes of GAE
Since 2015, the efficacy of GAE in reducing VAS, WOMAC, and KOOS scores has been demonstrated in multiple studies. These include:
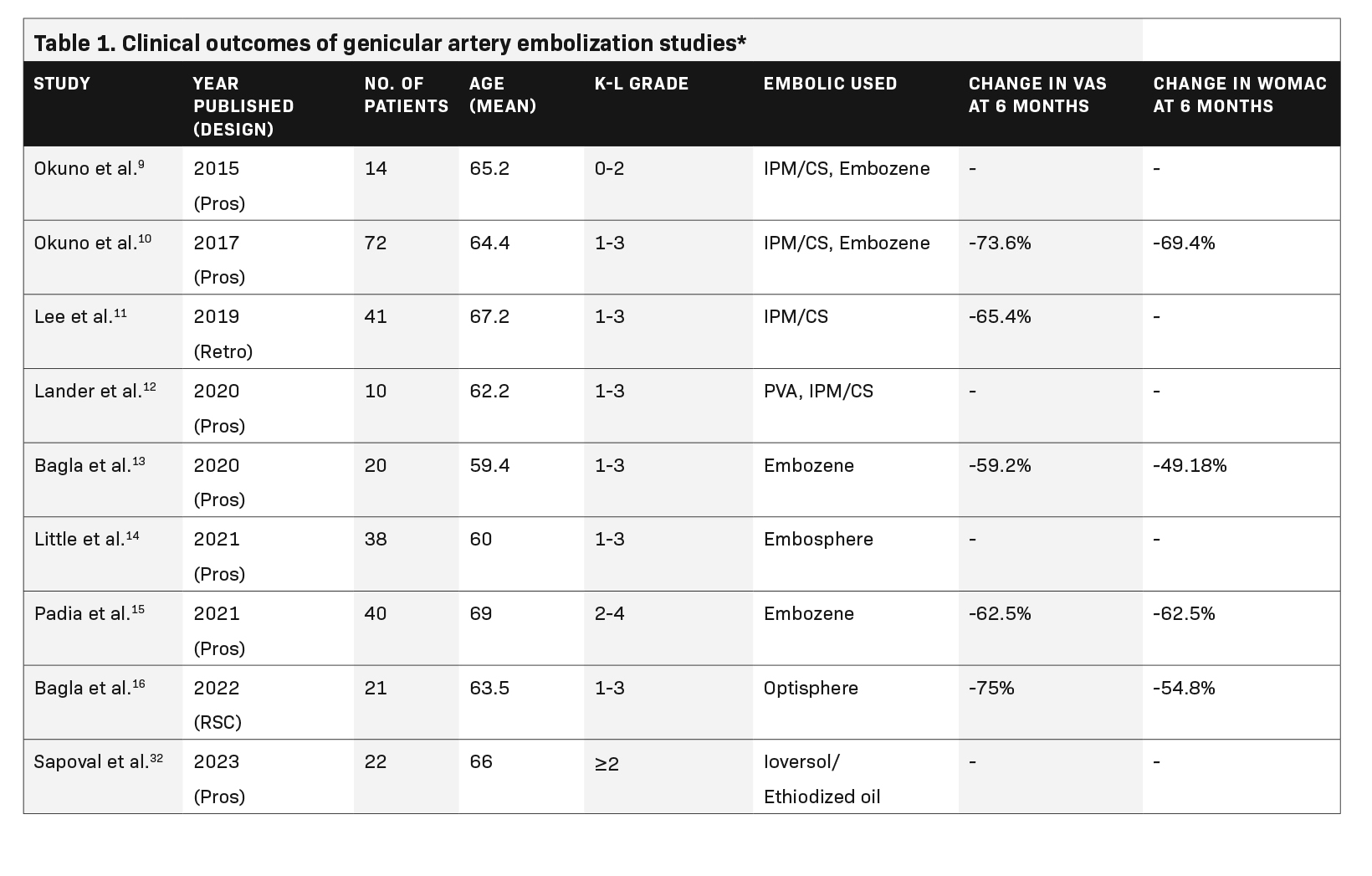
- A 2015 prospective pilot study of 11 patients that found significant improvement in WOMAC scores at 12 months compared to baseline.9
- A 2017 prospective study of 72 patients demonstrated significant improvement in WOMAC scores at 12 months, as well as WORMS scores at baseline and 2 years postprocedure showing significant improvement in synovitis.10
- A 2019 retrospective study of 41 patients with severe and mild-to-moderate knee OA demonstrated significant improvement through 10 months. In the severe OA group, the VAS score returned to baseline at the 3-month follow-up.11A detailed breakdown of these and five other studies showing the impact of GAE on knee OA is provided in Table 1.
Future Steps and Possible Limitations in Implementation
These studies have included only patients with mild-to-moderate (KL 1-3) OA. Less is known about the outcomes of GAE in severe OA with KL 4. Moreover, studies comparing TKA or intra-articular steroids with GAE and different types of embolic agents could provide more explicit evidence. Results from the MOTION34(GAE vs intra-articular steroids) and GAUCHO (IPM/CS vs microspheres) trials, for example, are expected in the near future.
Current literature comprises single-arm and small, randomized studies. In addition, some studies have also reported positive placebo effects with sham procedures. Therefore, the ongoing GENESIS 2 (double-blinded randomized sham-controlled) trial with large sample size could provide robust results. Outcomes in most of the studies have been reported based on subjective scoring methods. For instance, pre- and postprocedure WORMS was evaluated in only one study.10
Furthermore, new objective measures identified by Taslakian et al21 and Badar et al29 are paving the way to better understanding of treatment effects and warrant further research. Studies involving patients from different geographical areas and ethnicities would also be helpful, as studies performed thus far have focused on only a few geographical regions.
References
Citation
A H, S JW, O BWA.Genicular Artery Embolization for Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Appl Radiol. 2024; (2):8-13.
March 5, 2024