Gadopiclenol Use in Stereotactic Localization Radiosurgery Procedures
Images
ELUCIREM™ (gadopiclenol) injection Important Safety Information
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures.
ELUCIREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of ELUCIREM in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
• Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2), or
• Acute kidney injury.
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age >60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended ELUCIREM dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration.
See Elucirem™ (gadopiclenol) injection full prescribing information and additional Important Safety Information located at the bottom of this article.
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are essential for enhancing the quality of MR scans to improve radiologists’ ability to identify pathology. However, the US Food and Drug Administration recommends “health care professionals should consider the retention characteristics of each agent when choosing a GBCA for patients who may be at higher risk for gadolinium retention. Minimize repeated GBCA imaging studies when possible, particularly closely spaced MRI studies. However, do not avoid or defer necessary GBCA MRI scans."1
In addition, the American College of Radiology recommendations include: "If the decision for an individual patient is made to use a GBCA for an MRI study, multiple factors need to be considered when selecting a GBCA, including diagnostic efficacy, relaxivity, rate of adverse reactions, dosing/concentration, and propensity to deposit in more sensitive organs such as the brain."2
One way to reduce this exposure is by using a GBCA that can be administered at a lower dose than a conventional GBCA, without impact on image quality.
That’s why Cleveland Clinic uses Elucirem (gadopiclenol) injection to image brain metastases for preoperative localization MR exams before stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). Elucirem is a highly stable macrocyclic GBCA and has the highest relaxivity in its class for MR imaging. It requires only half the gadolinium dose of conventional, nonspecific GBCAs, addressing practitioners’ concerns about gadolinium exposure.3,4
The administration of a GBCA for MR imaging improves the contrast between lesions and surrounding tissues by accelerating the relaxation of protons through interaction with gadolinium atoms.5 Gadopiclenol delivers twice as much interaction as other GBCAs, resulting in the highest relaxivity among nonspecific GBCAs.5 Elucirem is used to identify lesions that have abnormal vascularity in the central nervous system (brain, spine and associated tissues) and the body (head and neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and musculoskeletal system).
“Using Elucirem, we can see lesions and delineate the margins of lesions with improved contrast enhancement,” said Jenny Wu, MD, MRMD, director of MRI Safety and a neuroradiologist at Cleveland Clinic.
GBCA Selection for Stereotactic Localization Radiosurgery Procedures
For these MR localization exams, Cleveland Clinic typically performs one of two scans: a volumetric postcontrast T1 scan with a 3D flash sequence, which is a spoiled gradient echo; or a T1 SPACE sequence, which is a 3D turbo spin echo sequence. The acquisition time is approximately seven minutes, and the exam is typically performed the day of treatment to reduce the time between imaging and treatment as much as possible.
When assessing GBCAs for these exams, Dr Wu first looks for stability. “We want a very stable molecule. Macrocyclic GBCAs tend to be more stable and less likely to let go of the gadolinium,” she said. “There’s less likely potential for gadolinium to accumulate and be deposited in the body, which is related to a lower risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.”
She also prioritizes patient tolerance and high relaxivity. “We want a contrast agent with a low rate of adverse drug reactions and high T1 relaxivity because there’s greater signal-to-noise ratio to better visualize the lesion,” said Dr Wu. “Increased T1 relaxivity also means you can use less of that agent to reduce gadolinium exposure to the patients.”
Clinical Experience with Elucirem
Cleveland Clinic used Elucirem to scan 100 patients for pre-SRS MRI localization exams to identify brain metastases. Dr Wu’s team found several advantages of Elucirem over the other GBCAs used for MRI procedures at Cleveland Clinic.
“The most important part of Elucirem in localization exams is that it has about two to three times more relaxivity than other contrast agents we use for MRI,” Dr Wu said. This was shown in the PICTURE study, which demonstrated the noninferiority of gadopiclenol at half dose to achieve similar clinical efficacy as a conventional dose of gadobutrol for MR imaging of the central nervous system.3
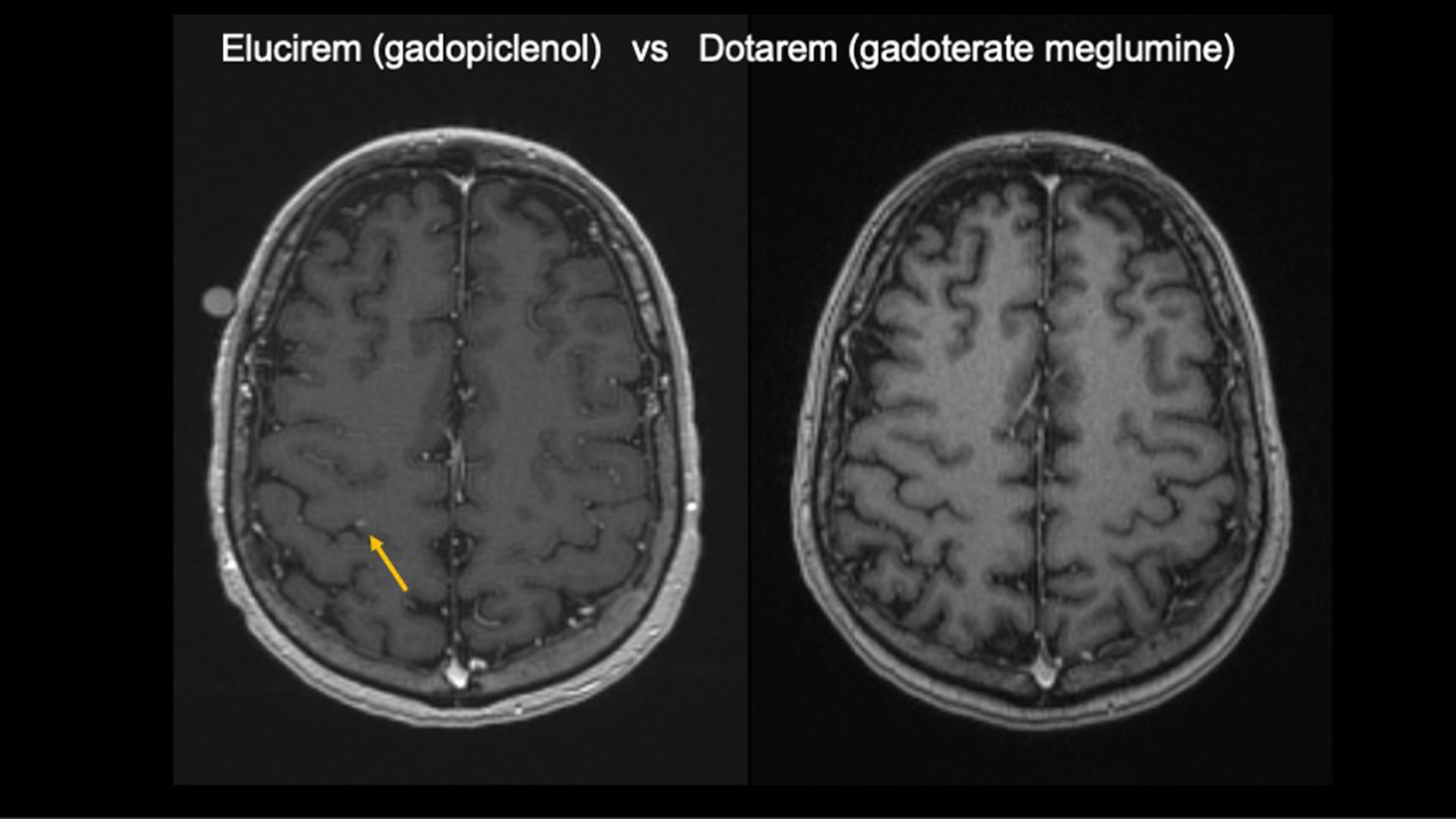
Gadopiclenol also helps Dr Wu detect different lesion types, which can influence treatment recommendations and determine eligibility for SRS.
Dr Wu also saw high patient tolerance for Elucirem in the 100 patients. “The safety profile is similar to other gadolinium-based contrast agents, and it has similar rates of adverse drug reactions,” she said.
Seeing the Clinical Advantages of Elucirem
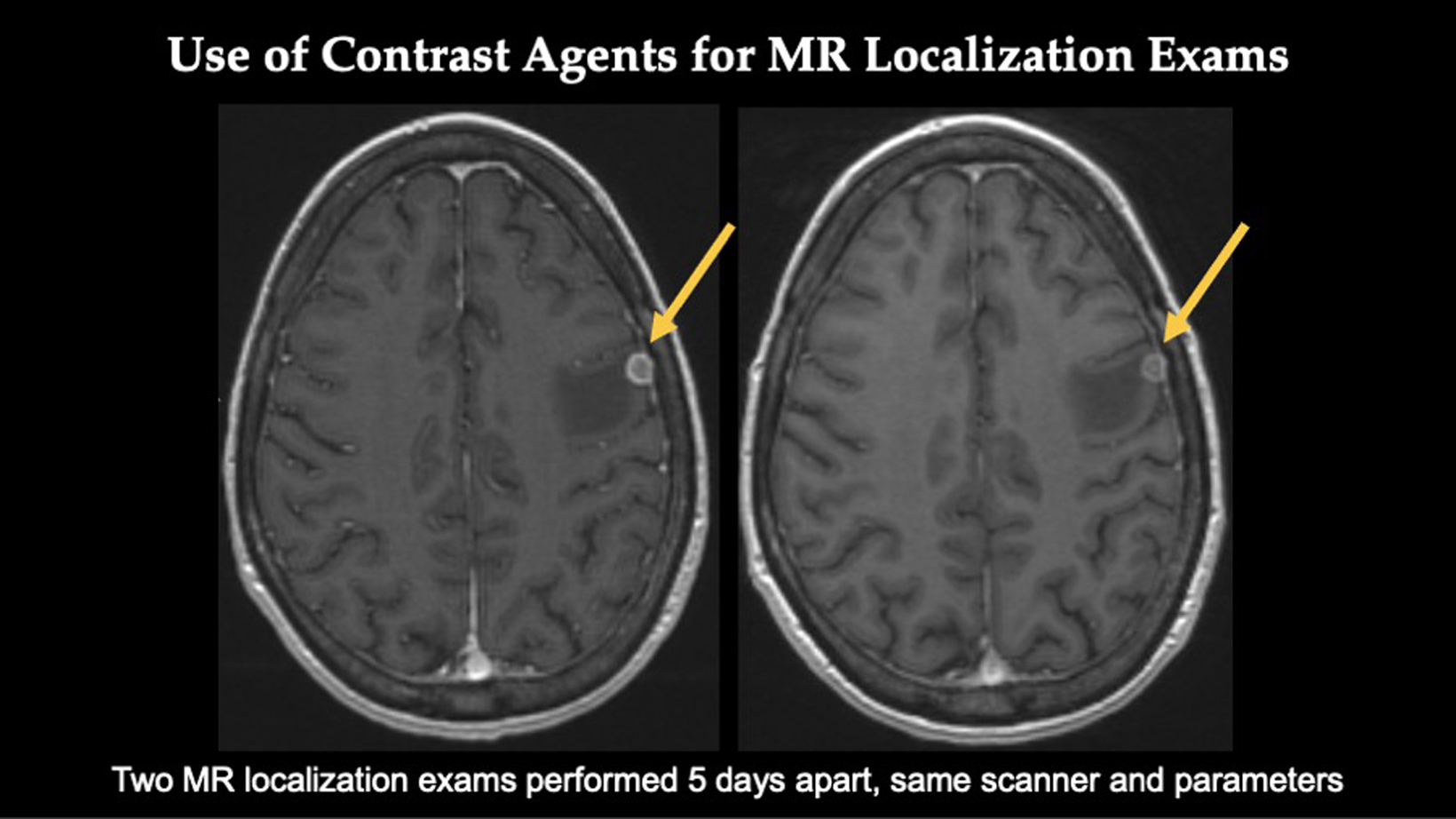
Dr Wu recently shared several case examples from the 100 patients scanned with Elucirem at Cleveland Clinic.
Dr. Wu and her colleagues noted that it’s critical to fully assess the ongoing pathology prior to stereotactic localization radiosurgery procedures. This comprehensive information drives the successful outcomes of this procedure and aids patient care and management.
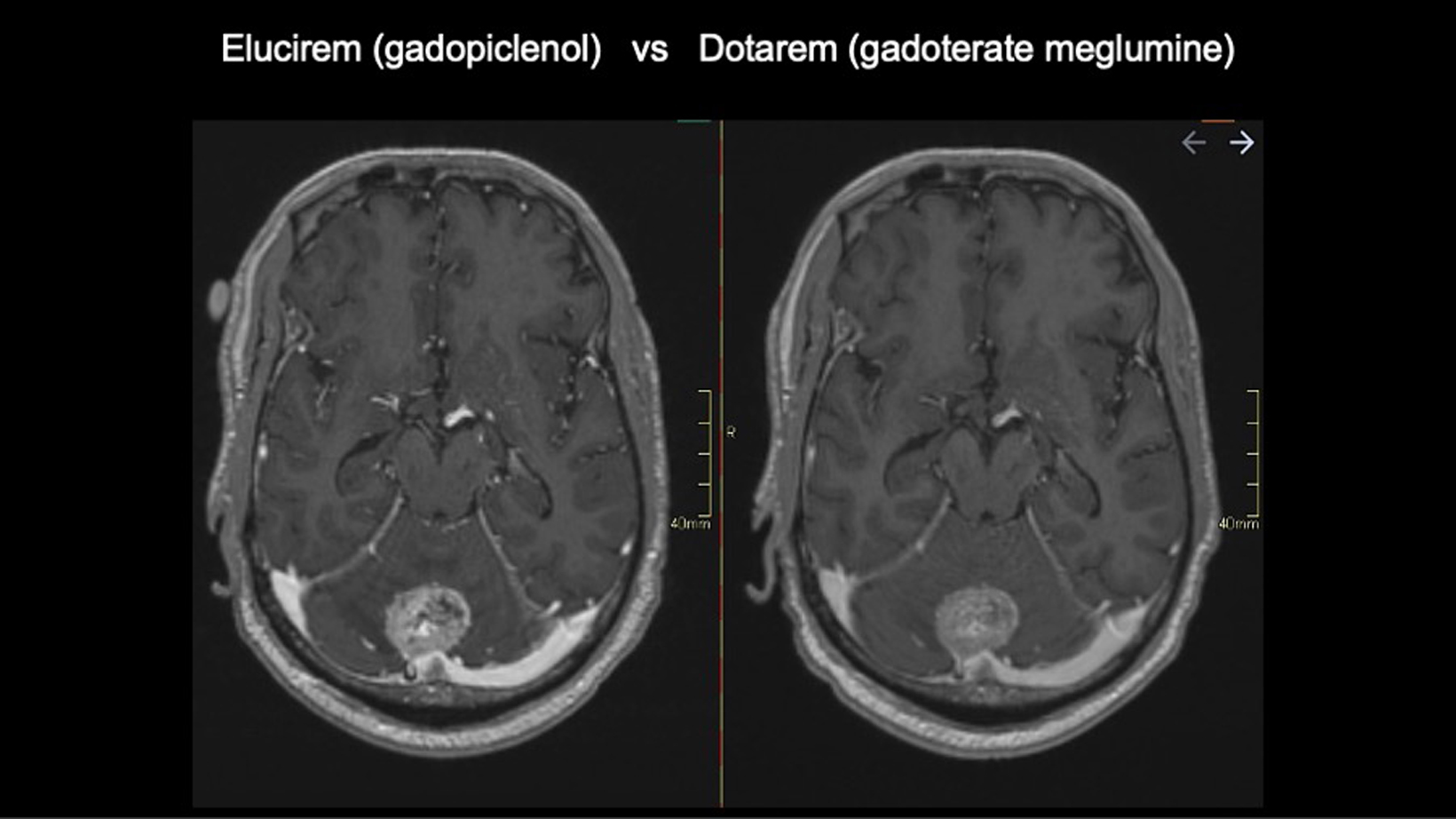
All patients were scanned with Elucirem after having a comparison scan with Dotarem (gadoterate meglumine) Injection.
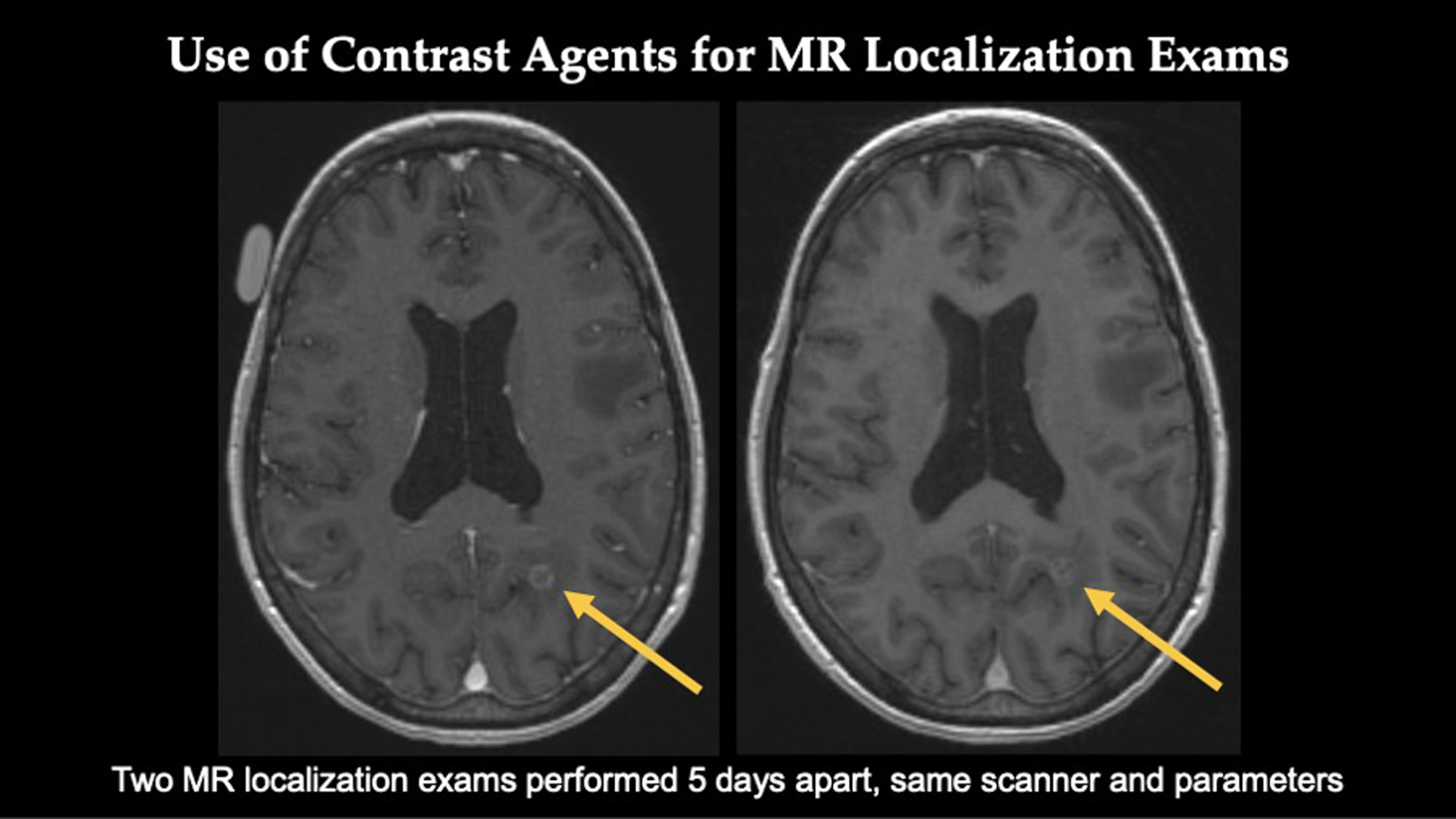
In this scan, the patient had two MRI localization exams performed five days apart with the same parameters on the same scanner.
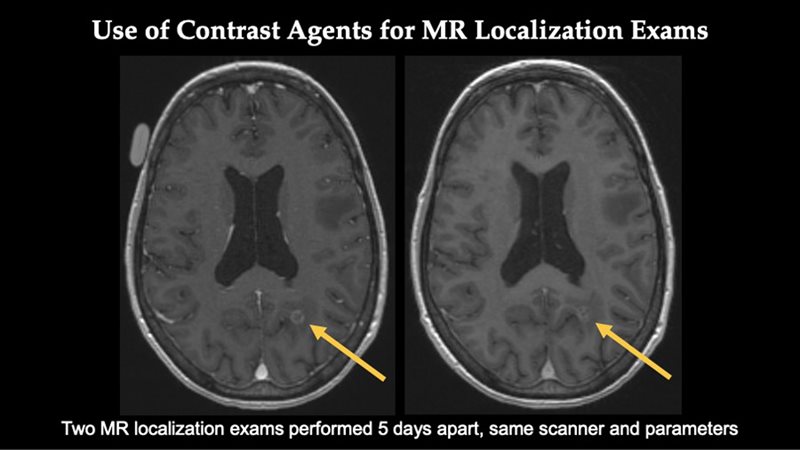
In this patient, Elucirem and Dotarem both show a lesion in the posterior fossa involving the cerebellum.
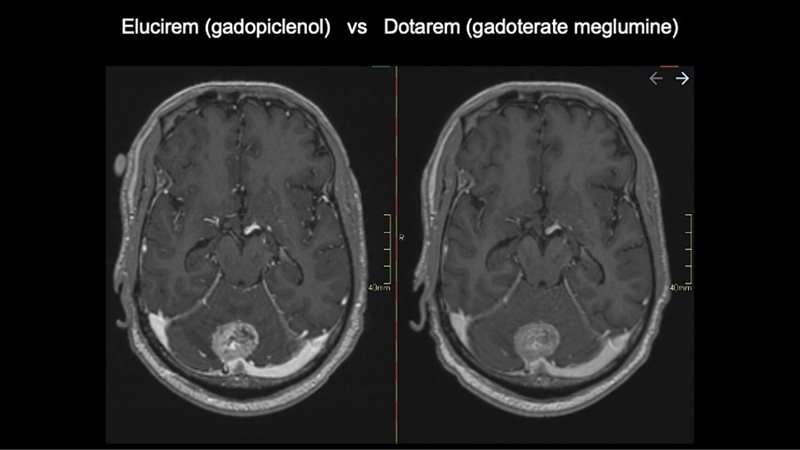
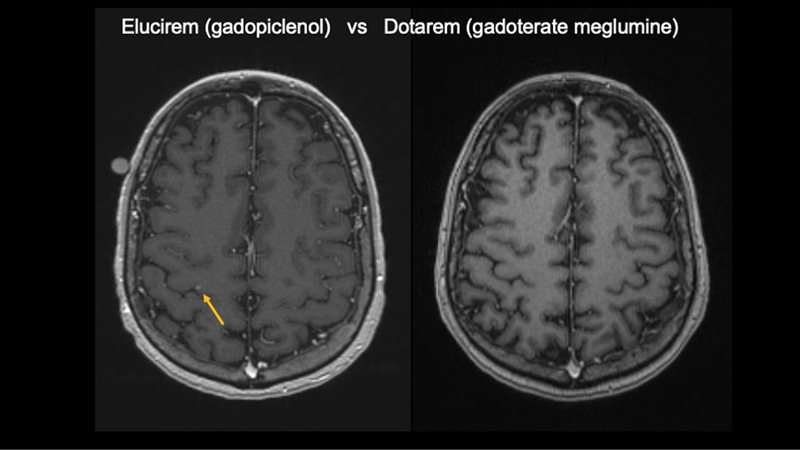
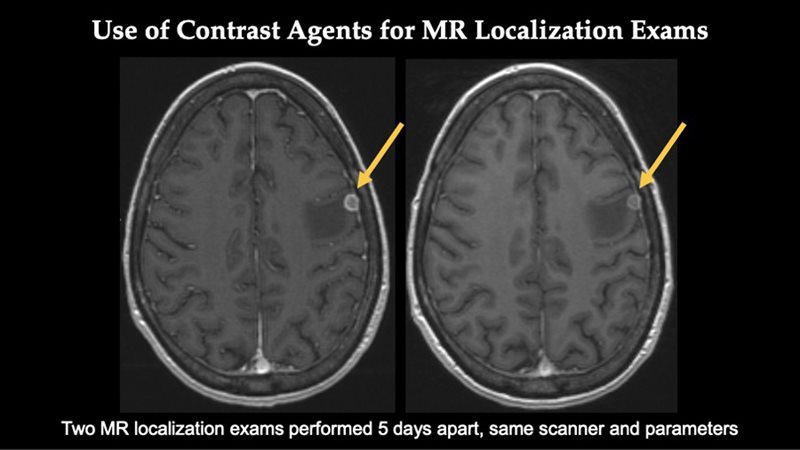
ELUCIREM™ (gadopiclenol) injection Important Safety Information
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures.
ELUCIREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of ELUCIREM in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
• Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2), or
• Acute kidney injury.
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age >60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended ELUCIREM dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration.
Indications and Usage
ELUCIREMTM (gadopiclenol) injection is indicated in adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect and visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in the central nervous system (brain, spine, and associated tissues), and the body (head and neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and musculoskeletal system).
Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients with history of hypersensitivity reactions to ELUCIREM.
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of ELUCIREM have not been established with intrathecal use. ELUCIREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
- Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of ELUCIREM among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: With GBCAs, serious hypersensitivity reactions have occurred. Before ELUCIREM administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to ELUCIREM.
- Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (e.g. brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen). While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
- Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent.
- Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Injection site reactions such as injection site pain have been reported in the clinical studies with ELUCIREM. Extravasation during ELUCIREM administration may result in tissue irritation. Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of ELUCIREM.
- Interference with Visualization of Lesions Visible with Non-Contrast MRI: As with any GBCA, ELUCIREM may impair the visualization of lesions seen on non-contrast MRI.
Adverse Reactions:
In clinical trials, the most frequent adverse reactions that occurred in > 0.2% of patients who received ELUCIREM included: injection site pain, headache, nausea, injection site warmth, injection site coldness, dizziness, and localized swelling.
Postmarketing Experience: Acute pancreatitis with onset within 48 hours after GBCA administration.
Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. There are no available data on ELUCIREM use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of ELUCIREM in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that 0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is excreted in breast milk.
- Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of ELUCIREM have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
- Geriatric Use: This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function.
- Renal Impairment: In patients with renal impairment, the exposure of gadopiclenol is increased compared to patients with normal renal function. This may increase the risk of adverse reactions such as NSF. No dose adjustment of ELUCIREM is recommended for patients with renal impairment.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see the full Prescribing Information, including the Medication Guide, for additional important safety information.
DOTAREM™ (gadopiclenol) injection Important Safety Information
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures.
DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of DOTAREM in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
• Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2), or
• Acute kidney injury.
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age >60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended DOTAREM dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration.
Indications and Usage
DOTAREMTM (gadoterate meglumine) injection is indicated in adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect and visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in the central nervous system (brain, spine, and associated tissues), and the body (head and neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and musculoskeletal system).
Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients with history of hypersensitivity reactions to DOTAREM.
Warnings and Precautions
- Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of DOTAREM have not been established with intrathecal use. DOTAREM is not approved for intrathecal use.
- Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: GBCAs increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of DOTAREM among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: With GBCAs, serious hypersensitivity reactions have occurred. Before DOTAREM administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to DOTAREM.
- Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (e.g. brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen). While clinical consequences of gadolinium retention have not been established in patients with normal renal function, certain patients might be at higher risk. These include patients requiring multiple lifetime doses, pregnant and pediatric patients, and patients with inflammatory conditions. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
- Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent.
- Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Injection site reactions such as injection site pain have been reported in the clinical studies with DOTAREM. Extravasation during DOTAREM administration may result in tissue irritation. Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of DOTAREM.
- Interference with Visualization of Lesions Visible with Non-Contrast MRI: As with any GBCA, DOTAREM may impair the visualization of lesions seen on non-contrast MRI.
Adverse Reactions:
In clinical trials, the most frequent adverse reactions that occurred in > 0.2% of patients who received DOTAREM included: injection site pain, headache, nausea, injection site warmth, injection site coldness, dizziness, and localized swelling.
Postmarketing Experience: Acute pancreatitis with onset within 48 hours after GBCA administration.
Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. There are no available data on DOTAREM use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of DOTAREM in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that 0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is excreted in breast milk.
- Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of DOTAREM have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age.
- Geriatric Use: This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function.
- Renal Impairment: In patients with renal impairment, the exposure of gadopiclenol is increased compared to patients with normal renal function. This may increase the risk of adverse reactions such as NSF. No dose adjustment of DOTAREM is recommended for patients with renal impairment.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please see the full Prescribing Information, including the Medication Guide, for additional important safety information.
GU06240111