Diagnosing hypoxia rapidly at bedside with transesophageal lung ultrasonography
When it is not feasible to transport patients to an imaging facility, such as patients undergoing surgery or those experiencing acute respiratory deterioration, transesophageal lung ultrasonography (TELU) may be the best immediate means to rapidly diagnose respiratory conditions. It provides point-of-care, real-time information to determine if a patient has developed acute hypoxemia. TELU can be used in any setting where a transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) probe is in place. It offers the ability to integrate both cardiac and pulmonary assessment in a single examination.
TELU is considered to be a novel technique to investigate hypoxemia, or abnormally low levels of oxygen in the blood, and has not been sufficiently validated for this use. However, physicians from the Université de Montréal in Quebec, Canada, believe that it is a valuable and powerful point-of-care imaging tool for emergency physicians, intensivists, and anesthesiologists who already use TEE on a regular basis. They describe the technique in detail in the November issue of the Canadian Journal of Anesthesia.
TELU should be used for the evaluation of acute hypoxemia when transthoracic ultrasound or other bedside imaging techniques are not available or are not feasible, as in the case of a patient with thoracic burns. It also is appropriate when transport of a patient to a radiology department or imaging modalities within an emergency department is not feasible due to the patient’s deteriorating condition.
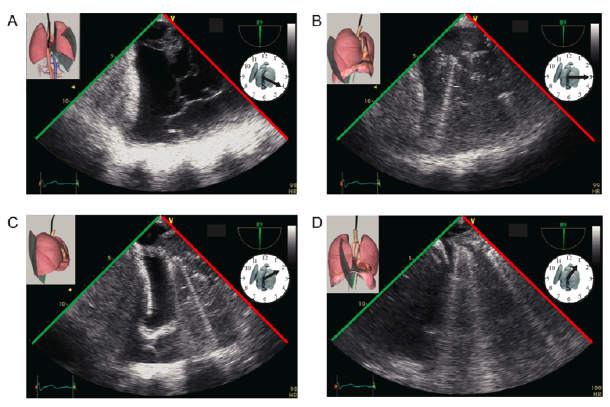
Figure 1. Pneumonia after lobectomy. Ultrasound images of the right lung after a lobectomy are shown using transesophageal echocardiography. (A) A right posterior complex pleural effusion is shown associated with lung consolidation as the ultrasound beam is moved clockwise to the (B) lateral and (C,D) anterolateral positions. In the anterior position, only B lines are seen. Courtesy of coauthor André Denault. Taken from Basic Transesophageal and Critical Care Ultrasound, with permission from CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group 2016.
TELU can also be used to diagnose specific lung pathologies, including pleural effusions, lung consolidation or alveolar interstitial syndrome. Lead author Yiorgos Alexandros Cavayas, MD, a critical care fellow in the division of critical care of the Montreal Heart Institute affiliated with the Université de Montréal, and co-authors provide a detailed explanation of the examination technique, and discuss both the advantages and limitations of TELU.
REFERENCE
- Cavayas YA, Girard M, Desjardins G, et al. Transesophageal lung ultrasonography: a novel technique for investigating hypoxemia. Can J Anesth. 2016 63;11:1266-1276. (doi: 10.1007/s12630-016-0702-2).
Citation
Diagnosing hypoxia rapidly at bedside with transesophageal lung ultrasonography. Appl Radiol.
November 3, 2016