Clinical Evidence Supports Dotarem® Injection for MR Imaging
Dotarem® (gadoterate meglumine) Injection Important Safety Information1
|
WARNING: NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF) Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. A void use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
|
Complete Dotarem® Important Safety Information below.
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) Utilization
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents are widely used to increase the contrast difference between normal and abnormal tissues.1 Also known as gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs), these MR contrast agents are generally referred to as T1 agents because they shorten T1 relaxation time, which can be referred to as the T1 relaxivity of the agent.
Relaxivity is an important criterion in selecting a GBCA. “It is a measure of how rapidly it affects the re-growing of longitudinal magnetization. This effect increases the brightness of T1 images and results in improved lesion detection and delineation. Radiologists widely utilize GBCAs to enhance tumors, vessels, or other structures,” says Kohkan Shamsi, MD, PhD, co-founder and principal of RadMD, an imaging consultancy.
GBCA Chelate Comparisons
There are several US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved GBCAs and, of those, there are two different types of chelates: linear, which partially wrap around the gadolinium (Gd) molecule, and macrocyclic, which form a “cage” around the gadolinium and are designed to tightly bind the molecule. Dotarem® (gadoterate meglumine) Injection and Gadavist® (gadobutrol) Injection are two commonly used macrocyclic GBCAs.2 Despite the difference in relaxivity between Dotarem® and Gadavist®, there is no measurable difference in clinical benefit observed between these two GBCAs despite quantitative mean lesion percentage enhancement being higher with gadobutrol.3 Dr. Shamsi agrees with those findings and believes that the small differences in relaxivity do not reflect in clinical efficacy.4
This has been shown in the REMIND Study, a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled intraindividual crossover study, which demonstrated “the non-inferiority of gadoterate meglumine [Dotarem®] versus gadobutrol [Gadavist®] for overall visualization and characterization of primary brain tumors.”1,3
Effective management of patients with pathology including brain tumors depends on accurate lesion detection and characterization. The primary objective of the REMIND study was to determine whether gadoterate meglumine is noninferior to gadobutrol for overall visualization and characterization of primary brain tumors.3
This noninferiority study included 279 patients. Both agents (0.1 mmol/kg of body weight dose) were administered and assessed with MR imaging at intervals of two to 14 days. MR scans were performed on patients using 1.5T systems at 15 centers and 3T systems at 12 centers. Dr. Shamsi notes that this is relevant, as nearly half of the investigational sites – and an increasing number of radiology facilities – are implementing 3T machines. The study also notes that there is a marginal decrease in the relaxivity of all contrast agents at higher field strengths.3 This study has shown the noninferiority of Dotarem® to Gadavist® on 1.5T and 3T MRI.3
Clinical Impact of GBCAs
With the primary end point of the REMIND study being overall lesion visualization and characterization, the agents were scored independently by three off-site readers on a four-point scale ranging from “poor” to “excellent.” Secondary end points were qualitative assessments (lesion border delineation, internal morphology, degree of contrast enhancement, diagnostic confidence), quantitative measurements (signal intensity), and safety (adverse events). All qualitative assessments were performed on-site.3
All three readers in the REMIND study scored lesion visualization and characterization as good or excellent for the majority of the patients (>90%) receiving either of the contrast agents.1,3 Additionally, in most cases, there was no preference among readers for either contrast agent regarding border delineation, internal morphology, and the qualitative degree of contrast enhancement, despite higher quantitative mean lesion percentage enhancement with gadobutrol.1,3
The study also confirmed a low incidence of immediate reported adverse events with both agents, as shown in multiple previous studies.3,5,6
“The results of this trial show that Dotarem® was noninferior to Gadavist® for visualization parameters, and the adverse event profile was similar. So, this study supports that there is no difference in clinical benefit between Dotarem® and Gadavist®,” says Dr. Shamsi.
REFERENCES3,7,8
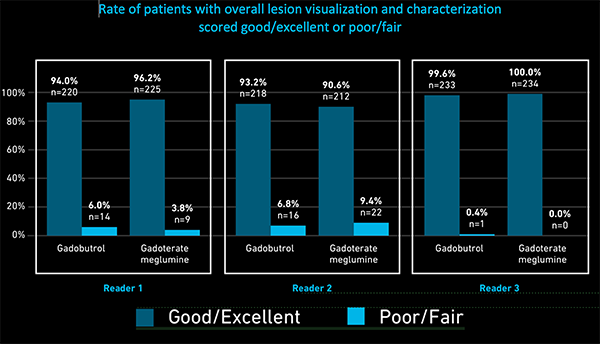
For all readers in the REMIND study, more than 90% presented with good or excellent overall lesion visualization and characterization with either of the two contrast agents. Additionally, in most cases, there was no preference of the among readers for either contrast agent regarding border delineation, internal morphology, and the qualitative degree of contrast enhancement, despite higher quantitative mean lesion percentage enhancement being higher with gadobutrol.1,3
GBCA Safety and Stability
The efficacy of most GBCAs is similar, with recent focus moving to safety and stability. Given the features and benefits of the utilization of MR contrast in MRI imaging, Dr. Shamsi says that in addition to efficacy, safety and stability should drive the selection of a contrast agent.
To date, the only known adverse health effect related to gadolinium retention is a rare condition called nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) that occurs in a small subgroup of patients with pre-existing kidney failure.2 Adverse events involving multiple organ systems have been reported in patients with normal kidney function.2 A causal association between these adverse events and gadolinium retention has not been established.2
To further address concerns about Gd retention, several recently published studies explored the retention of Gd in various animal tissues. While experts may agree that levels of Gd retention can vary among macrocyclic agents, recent peer-reviewed animal studies demonstrate the complexities of the topic and that a myriad of uncertainties remain. Also, notably, the clinical significance, if any, of Gd retention in patients with normal renal function has not been demonstrated.5, 9-13 Tissue retention of Gadolinium in animal models likely depends on the timeframe investigated, with washout of macrocyclic GBCAs continuing for at least one year.10
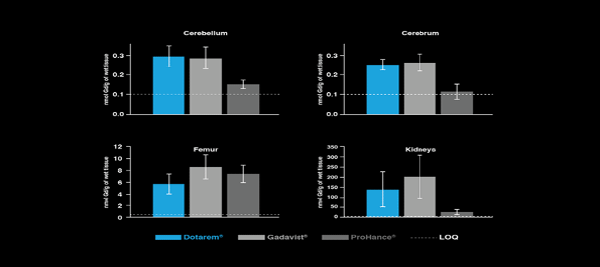
Bussi et al. compared Gd levels in blood, cerebrum, cerebellum, liver, femur, kidneys, and skin after multiple exposures of rats to Dotarem®, Gadavist®, and ProHance®, and found that at 28 days (4 weeks), there was less Gd retention with ProHance than with Dotarem® or Gadavist in most tissues. However, Dotarem® had significantly less Gd presence in the femur, where higher levels of Gd deposition were noted for all the GBCAs.9
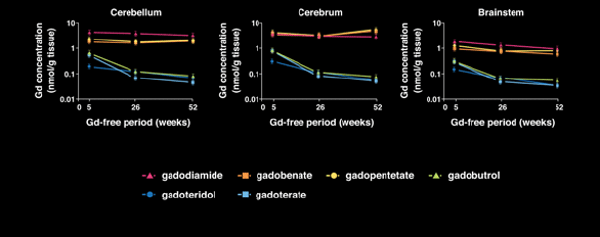
Jost et al. examined rats that received multiple administrations of one of the three macrocyclic agents on the market (ProHance, Dotarem® and Gadavist) at 5, 26 and 52 weeks following administration. This study confirmed that after 5 weeks, gadolinium concentrations in the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem were higher with Dotarem® when compared to ProHance, similar to the study by Bussi et al. However, while the washout of all the macrocyclic agents were similar, after 26 and 52 weeks, Dotarem® measured the lowest total concentration of retained gadolinium across brain regions studied, illustrating a continuous and long-term elimination.10
GBCA stability plays an important role in selection, and safety can be dependent on structure and stability of the agent. “Dotarem® is a macrocyclic as well as an ionic agent, which supports higher thermodynamic and kinetic stability,” says Dr. Shamsi. The high molecular stability of the agent can minimize the risk of gadolinium release from the GBCA molecule.14,15
Dotarem® has gained a significant share of the U.S. market and continues to be a leading choice of radiologists and technologists, with no unconfounded cases of NSF reported to date. 5,14
GBCA Selection for Clinical Use
When institutions are selecting an MR contrast agent, physicians with knowledge and experience about GBCAs, current related issues, and the latest FDA Safety Communications should be part of the decision-making team. Therefore, when a risk-benefit analysis supports the use of contrast with MRI, stability is an important consideration when selecting from among the currently available GBCAs.
Overall, Dr. Shamsi says, macrocyclic agents provide diagnostic benefits in the general population, and he supports the FDA’s requirement that the GBCA medication guide be given to patients to explain the risks of contrast-enhanced MRI.
“Gadolinium-based contrast agents have been approved for clinical use for over 30 years and they provide immense diagnostic benefit to the patients,” says Dr. Shamsi. “They play a very important role in diagnosing diseases and improving patient management.”
Since its release in 1989, Dotarem® has been a leading contrast agent in Europe, Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and South America. Dotarem® Injection received FDA approval in 2013, becoming the first macrocyclic, ionic, gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA) in the United States. In just seven years, it has become the No. 2 MR contrast agent in the U.S. and is currently No. 1 in the world, with more than 100 million doses administered in 70 countries.16
References
- Xiao, Y., Paudel, R., Liu, J., Ma, C., Zhang, Z., & Zhou, S. (2016). MRI contrast agents: Classification and application (Review). International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 38, 1319-1326. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2744.
- FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns that gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are retained in the body; requires new class warnings. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-fda-warns-gadolinium-based-contrast-agents-gbcas-are-retained-body
- Maravilla K et al. Comparison of Gadoterate Meglumine and Gadobutrol in the Diagnosis of Primary Brain Tumors: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Intraindividual Crossover Study (the REMIND Study). 2017 June 29. doi: 10:3174/ajnr.A5316. [Epub ahead of print].
- Gadavist [package insert]. Whippany, NJ: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.; August 2020.
- de Kerviler E et al. Adverse Reactions to Gadoterate Meglumine: Review of Over 25 Years of Clinical Use and More Than 50 Million Doses. Invest Radiol. 2016;51:544-551.
- Endrikat J et al. Safety of gadobutrol: results from 42 clinical phase II to IV studies and postmarketing surveillance after 29 million applications. Invest Radiol 2016;51: 537–43 CrossRef Medline.
- Anzalone N, Scarabino T, Venturi C, et al. Cerebral neoplastic enhancing lesions: multicenter, randomized, crossover intraindividual comparison between gadobutrol (1.0M) and gadoterate meglumine (0.5M) at 0.1 mmol Gd/kg body weight in a clinical setting. Eur J Radiol 2013;82:139 –45.
- Saake et al. MRI in multiple sclerosis: an intra-individual, randomized and multicentric comparison of gadobutrol with gadoterate meglumine at 3 T. Eur Radiol. 2016;26:820-828.
- Bussi S et al. Differences in Gadolinium Retention After Repeated Injections of Macrocyclic MR Contrast Agents to Rats J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47:746-752.
- Jost G et al. Long-term Excretion of Gadolinium-based Contrast Agents: Linear versus Macrocyclic Agents in an Experimental Rat Model: Radiology. 2019;290:340-348.
- Behzadi AH et al. Immediate Allergic Reactions to Gadolinium-based Contrast Agents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology. 2018;286:471-482.
- McDonald RJ et al. Comparison of Gadolinium Concentrations within Multiple Rat Organs after Intravenous Administration of Linear versus Macrocyclic Gadolinium Chelates. Radiology. 2017;285:536-545
- McDonald JS et al. Radiology. Acute Adverse Events Following Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent Administration: A Single-Center Retrospective Study of 281,945 Injections. 2019; Jul 2;182834.
- Dotarem® [package insert]. Princeton, NJ: Guerbet LLC; Oct 2019.
- Frenzel T et al. Stability of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents in human serum at 37°C. Invest Radiol. 2008; 43:817-828.
- Data on File. Guerbet LLC based on through Q1 2020.
Editor’s Note:
Guerbet LLC., the US affiliate of Guerbet, is a pharmaceutical and medical device company that offers a comprehensive range of specialized solutions for diagnostic and interventional radiology. The company’s portfolio includes products, services, and digital software solutions for MRI, CT, and interventional radiology (including the cath lab and women’s health). Driven by its commitment to advance radiology, Guerbet has designed a range of interconnected contrast imaging solutions to enhance decision making at all points of a patient’s journey — diagnosis, treatment, documentation, and follow-up — so that clinicians can focus on what matters most: quickly and efficiently improving the patient experience.
Applied Radiology spoke with Kohkan Shamsi, MD, PhD, co-founder and principal of RadMD, about his experience with the utilization of gadolinium-based contrast agents. RadMD provides expertise-based services related to imaging in clinical trials including consulting, training, and sourcing highly trained and experienced independent image reviewers from its global group of nearly 600 physicians. As a radiologist with more than 25 years of clinical development experience for drugs and devices, Dr. Shamsi has conceptualized, coordinated, and executed more than 100 multi-center, international clinical trials in the areas of oncology, cardiology, neurology and contrast agent for MRI, CT, and radiopharmaceuticals that led to approval of several contrast agents globally. He has contributed towards development of guidelines for clinical development of contrast agents for the FDA and EMA, and the FDA draft imaging guidance for use of imaging in oncology trials.
Dotarem® (gadoterate meglumine) Injection Important Safety Information
|
WARNING: NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF) Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. A void use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal ordebilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
|
Indications and Usage
DOTAREM® (gadoterate meglumine) injection is a prescription gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain (intracranial), spine and associated tissues in adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to detect and visualize areas with disruption of the blood brain barrier (BBB) and/or abnormal vascularity.
Contraindications
History of clinically important hypersensitivity reactions to DOTAREM®.
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with DOTAREM®, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations. Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died. In most cases, initial symptoms occurred within minutes of DOTAREM® administration and resolved with prompt emergency treatment.
- Before DOTAREM® administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to DOTAREM®.
- Administer DOTAREM® only in situations where trained personnel and therapies are promptly available for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, including personnel trained in resuscitation.
- Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by brain, skin, kidney, liver and spleen. The duration of retention also varies by tissue, and is longest in bone. Linear GBCAs cause more retention than macrocyclic GBCAs.
- Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established. Adverse events involving multiple organ systems have been reported in patients with normal renal function without an established causal link to gadolinium retention.
- Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
- Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of DOTAREM®. Extravasation into tissues during DOTAREM® administration may result in tissue irritation.
Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions associated with DOTAREM® in clinical trials were nausea, headache, injection site pain, injection site coldness and rash.
- Serious adverse reactions in the Post marketing experience have been reported with DOTAREM®. These serious adverse reactions include but are not limited to: arrhythmia, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, pharyngeal edema, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, coma and convulsion.
Use in Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. The human data on the association between GBCAs and adverse fetal outcomes are limited and inconclusive. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk of fetal exposure to GBCAs.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of gadoterate in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that 0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is present in breast milk.
- Pediatric Use: The safety and efficacy of DOTAREM® at a single dose of 0.1 mmol/kg has been established in pediatric patients from birth (term neonates ~ 37 weeks gestational age) to 17 years of age based on clinical data. The safety of DOTAREM® has not been established in preterm neonates. No cases of NSF associated with DOTAREM® or any other GBCA have been identified in pediatric patients age 6 years and younger.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088. Please see the full Prescribing Information, including the patient Medication Guide, for additional important safety information. For more information, visit https://www.guerbet.com/products-solutions/
GU05210087
Citation
. Clinical Evidence Supports Dotarem® Injection for MR Imaging. Appl Radiol.
July 12, 2021