AI Reduces DBT Workload by Identifying Normal Scans
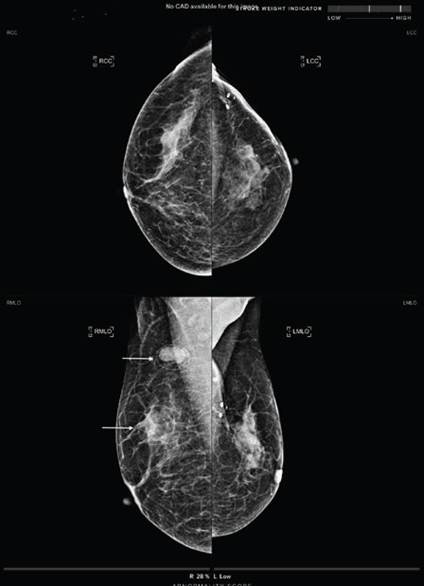 An AI system for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) trained on exams from imaging facilities filtered out cancer-free exams, leading to lower recall rates and fewer exams in a simulated workflow. Published in Radiology, the retrospective study of 5,182 DBT screening exams reduced radiologist workload by 39.6% while maintaining noninferior sensitivity. By removing cancer-free exams, the number of women who would have been recalled also dropped by 25%.
An AI system for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) trained on exams from imaging facilities filtered out cancer-free exams, leading to lower recall rates and fewer exams in a simulated workflow. Published in Radiology, the retrospective study of 5,182 DBT screening exams reduced radiologist workload by 39.6% while maintaining noninferior sensitivity. By removing cancer-free exams, the number of women who would have been recalled also dropped by 25%.
An analysis of the AI false-positive findings showed that almost 70% were occult at mammography. AI performance was stable across age groups, ethnicity and body mass index, suggesting the AI model may be applicable to diverse populations.
With the simulated worklist reduction for the mean reader, specificity increased 6.4% and recall rates decreased 5%, suggesting the potential contribution of AI in these cases and support for AI to augment human decision making. The authors suggest that AI first be used in repetitive tasks.
The authors conclude that implementing this type of AI model in clinical practice could reduce both radiologist workload and fatigue, improve workflow, further facilitate the use of DBT for screening and reduce unnecessary patient recalls and exposure to radiation. Future research, they say, should evaluate multiple DBT manufacturers.