Qure.ai’s AI-Based Solution for Quantifying and Characterizing Lung Nodules Gets FDA Clearance
Images
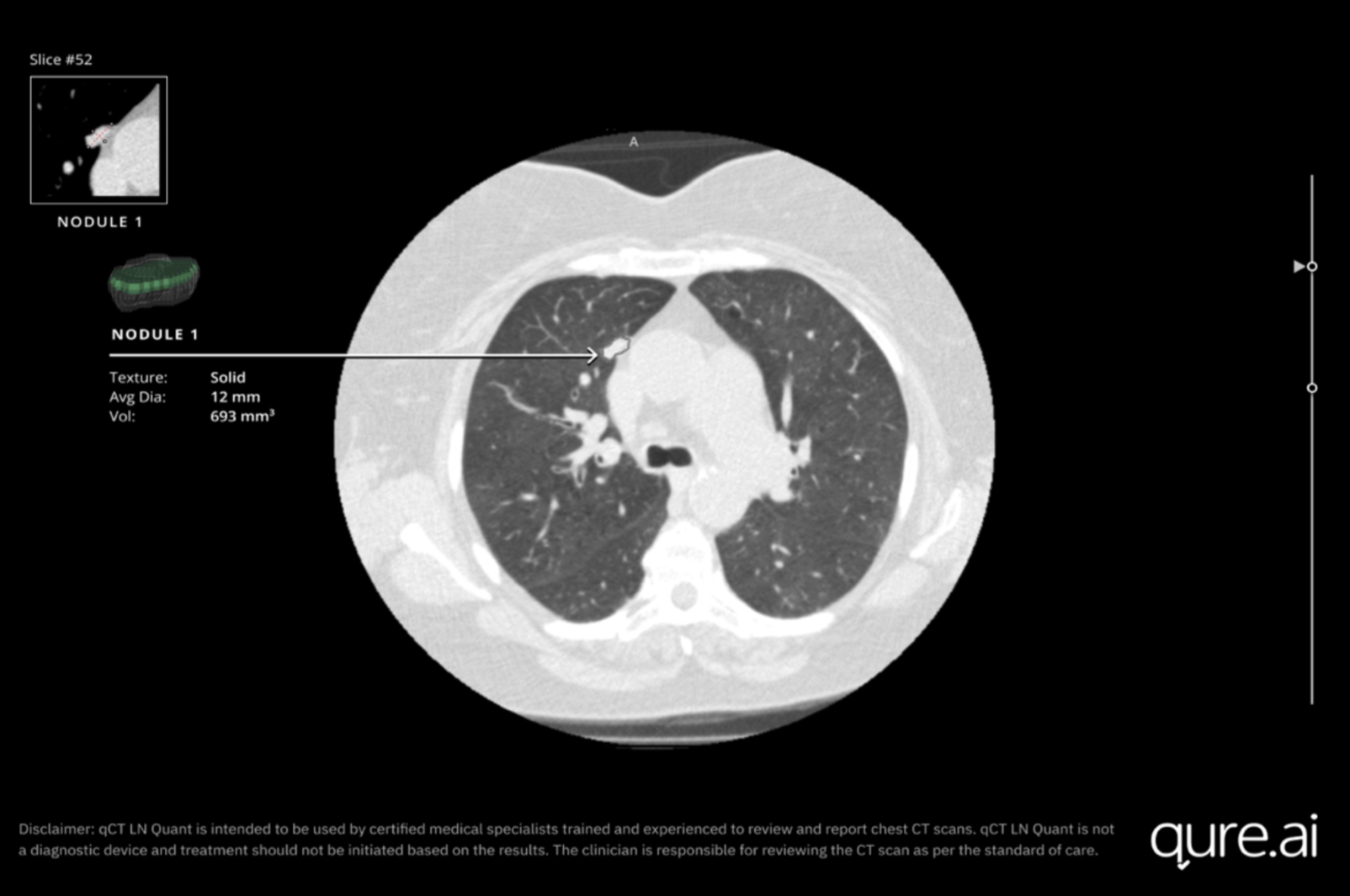
Qure.ai announced 510(k) FDA clearance for its AI-powered chest CT solution – qCT LN Quant. The new AI solution is now available to support radiologists and pulmonologists in analyzing lung nodules on non-contrast chest CT scans and tracking volumetric growth as part of progression monitoring.
qCT LN Quant joins the Qure.ai US AI-powered Lung Cancer care continuum, featuring end-to-end AI solutions to identify, measure, manage, and monitor lung health. These help to support clinicians at healthcare institutions and drive early detection. This includes ‘qXR LN’ for the early detection and localization of lung nodules on chest X-rays to support early lung cancer detection beyond traditional CT-based screening initiatives, and ‘qTrack,’ a multi-modality lung nodule management platform that integrates with Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) to help find, report, collaborate, and prioritize lung cancer patient cases.
qCT LN Quant offers advanced quantitative characterization of solid lung nodules, measuring average, short-axis, long-axis, and effective diameters. It allows clinicians to analyze morphological data across single or multiple thoracic studies, including estimated volume doubling time and tracking of nodules over several time points. Furthermore, it generates detailed 2D and 3D reconstructions, Brock malignancy risk scores, and Fleischner Society guidelines-based management suggestions to support consistent and reliable clinical decision-making. qCT LN Quant is potentially eligible under two CPT codes for reimbursement – tissue quantification CPT 0722T for CT and 3D reconstruction code.
“We are delighted to showcase qCT LN Quant at the American Association for Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology (AABIP) conference in North Carolina,” states Bhargava Reddy, Chief Business Officer, Oncology at Qure.ai. “This FDA clearance marks a significant milestone for Qure.ai’s mission to enhance lung cancer care in the United States. Already, we’re starting to see the power of AI for incidental pulmonary nodule detection using chest X-ray, across multiple care settings, to boost lung surveillance, especially in states with low lung cancer screening CT uptakes. Now, we have the next stage solution in the AI-optimized patient pathway, to evaluate lung nodules on at-risk patient CT scans, giving precise quantitative characterization, plus tracking volumetric growth over time.”
Javier Zulueta, MD, Chief, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at Mount Sinai Morningside, New York, comments, “Medical imaging AI holds immense potential in the battle against lung cancer in the United States. It is great to see the breadth of FDA clearances rolling in to enable the exploration and activation of algorithms that can support radiologists and pulmonologists. This will help to detect lung nodules earlier using chest X-ray, and also analyze them in detail on chest CT.”