Neuroimaging Study Finds Widespread Brain Structure Differences in Youth With Conduct Disorder
Images
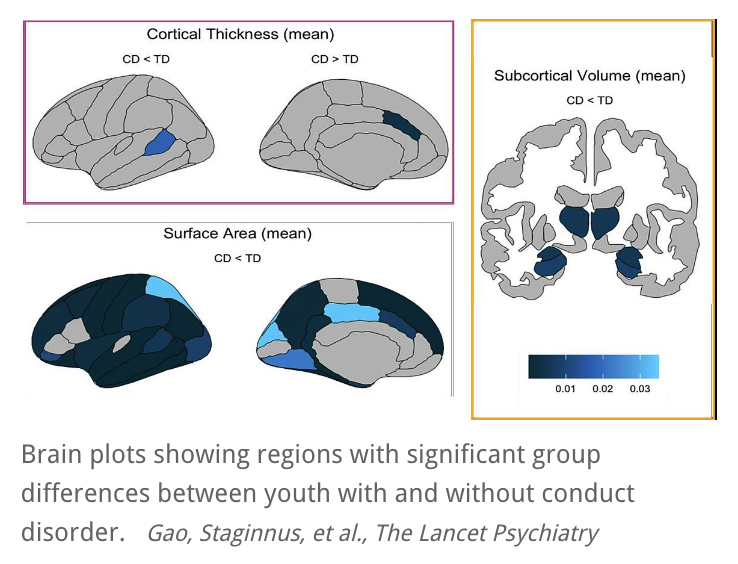
A neuroimaging study of young people who exhibit a persistent pattern of disruptive, aggressive and antisocial behavior — known as conduct disorder — has revealed extensive changes in brain structure. The most pronounced difference was a smaller area of the brain’s cerebral cortex, which is critical for many aspects of behavior, cognition and emotion. The study, co-authored by researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), is published in The Lancet Psychiatry.
“Conduct disorder has among the highest burden of any mental disorder in youth. However, it remains understudied and undertreated. Understanding brain differences associated with the disorder takes us one step closer to developing more effective approaches to diagnosis and treatment, with the ultimate aim of improving long-term outcomes for children and their families,” said co-author Daniel Pine, MD, chief of the Section on Development and Affective Neuroscience in NIH’s National Institute of Mental Health. “Critical next steps are to follow children over time to determine if differences in brain structure seen in this study are a cause of conduct disorder or a long-term consequence of living with the disorder.”
A collaborative group of researchers examined standardized MRI data from youth ages 7 to 21 who had participated in 15 studies from around the world. Analyses compared the surface area and thickness of the cerebral cortex and the volume of deeper subcortical brain regions between 1,185 youth diagnosed with conduct disorder and 1,253 youth without the disorder. Additional analyses compared the cortical and subcortical brain measures between boys and girls, age of symptom onset (childhood vs. adolescence), and level of empathy and other prosocial traits (high vs. low).
Youth with conduct disorder had lower total surface area across the cortex and in 26 of 34 individual regions, two of which showed significant changes in cortical thickness. Youth with conduct disorder also had lower volume in several subcortical brain regions, including the amygdala, hippocampus and thalamus, which play a central role in regulating behaviors that are often challenging for people with the disorder. Although some of these brain regions, like the prefrontal cortex and amygdala, had been linked to conduct disorder in previous studies, other regions were implicated in the disorder for the first time.
The associations with brain structure did not differ between boys and girls and were seen across conduct disorder subgroups based on age of onset and level of prosocial traits. Youth who exhibited signs of a more severe form of the disorder, indicated by a low level of empathy, guilt, and remorse, showed the greatest number of brain changes.
These findings from the largest, most diverse, and most robust study of conduct disorder to date are consistent with a growing body of evidence that the disorder is related to the structure of the brain. The study also provides novel evidence that brain changes are more widespread than previously shown, spanning all four lobes and both cortical and subcortical regions. These findings offer new avenues for investigating potential causal links between differences in brain structure and symptoms of conduct disorder and for targeting brain regions as part of clinical efforts to improve diagnosis and treatment.