CMS Establishes National Payment for Innovative Prostate Cancer Mapping Technology
Images
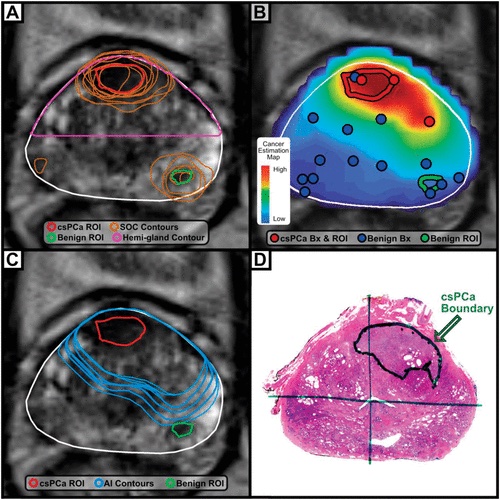
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has assigned a national payment rate for Unfold AI, an innovative prostate cancer mapping technology from Avenda Health. Additionally, effective July 1, 2024, the American Medical Association (AMA) implemented a new Category III code for reimbursement on services related to the use of Unfold AI, marking a major step forward in making this technology more widely available to patients.
Category III codes allow data collection for new or emerging healthcare approaches and establish the foundation that facilitates reimbursement pathways for healthcare providers. The code for Unfold AI, 0898T, enables healthcare providers to bill for these non-invasive prostate cancer estimation maps, which are derived from advanced analysis of image-guided fusion biopsy and pathology. This includes visualization of tumor margins, margin determination and physician interpretation and reporting.
Medicare reimbursement is determined by the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS), assigning the procedure to the appropriate Ambulatory Payment Classification (APC) for diagnostic tests and related services. This is a standardized approach for outpatient settings, while reimbursement for physician services and commercial payers will depend on individual contractual agreements and geographic variations. These designations underscore the growing recognition of AI technology in enhancing prostate cancer care.
“Receiving the new CPT code and national payment rate for Unfold AI is an important development in making advanced personalized prostate cancer care accessible to more patients,” said Avenda Health COO Brit Berry-Pusey, PhD. “This recognition by the AMA and CMS validates the transformative potential of our technology in improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.”
Last month, a study conducted at UCLA was published in The Journal of Urology, demonstrating Unfold AI's ability to identify the extent of prostate cancer with 84% accuracy. The study showed that AI-assisted diagnosis improves the ability of physicians by 45 times compared to standard human-driven identification methods. This means more accurate diagnoses and targeted treatments, potentially reducing the need for full-gland removal and its associated side effects.