CMR Shows Myocardial Fibrosis In Patients With Hypertension Is Linked To Worse Outcomes
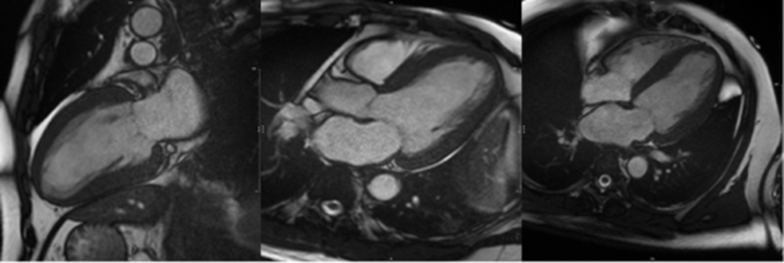
CMR of a patient showing evidence of myocardial hypertrophy (thickening
of heart muscles) due to hypertension. Credit: National Heart Centre Singapore.
A recent study conducted by the National Heart Centre Singapore (NHCS) discovered that myocardial fibrosis detected non-invasively using cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) is associated with worse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with hypertension. Myocardial fibrosis is an important prognostic marker in the development of adverse cardiovascular events, such as heart failure and death.
In this prospective and observational study, titled REMODEL (Response of the Myocardium to Hypertrophic Conditions in the Adult Population)5 led by Associate Professor Calvin Chin, Clinician Scientist and Senior Consultant from the Department of Cardiology at NHCS, CMR was performed in close to 800 patients with hypertension. The patients were followed up for adverse cardiovascular events over an average period of more than three years. CMR is a useful diagnostic tool which detects heart structural abnormalities and quantifies fibrosis without the invasive sampling of heart muscle tissues.
Myocardial fibrosis typically happens in patients with previous heart attacks. Correspondingly, patients in the REMODEL study did not have previous heart attacks, hence any occurrence of myocardial fibrosis have been deduced to that of patient’s susceptibility to blood pressure, and other reasons such as genetic predisposition and other medical co-morbidities like diabetes.
“Although anecdotal reports have previously shown the presence of heart muscle scarring in patients with hypertension, this is the first study that confirms the adverse association between scarring of heart muscle and the cardiovascular outcomes in patients with hypertension. We found that heart muscle scarring is a stronger predictor of adverse outcomes even after correcting for patients’ age, sex and systolic blood pressures,” said Assoc Prof Calvin Chin, who is also the Director of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging at NHCS.
The research team further found that the heart muscle response to hypertension in patients is heterogeneous or diverse, whereby while two patients may have similar blood pressure, their myocardial characteristics can be different. This presents opportunities to tailor and personalise treatment for hypertensive patients who have heart muscle scarring to reduce potential risk of future cardiovascular events, beyond lowering their blood pressure and achieving their blood pressure targets.
Following these findings that were published this year in the medical Journal Hypertension, Assoc Prof Calvin Chin and the team are now into the next phase of an ongoing trial REVERSE-LVH6 to assess the potential of reversing heart muscle scarring, through the use of specific therapies targeted at fibrosis in patients with hypertensive heart disease. REVERSE-LVH is a randomised controlled study to compare the efficacy of medications in regressing myocardial fibrosis. Patients recruited in the study would undergo CMR after a year to quantity the amount of myocardial fibrosis detected before and after treatment.
“Using CMR, a non-invasive tool to detect fibrosis has potential to improve risk-stratification of patients with hypertension. Targeted anti-fibrotic intervention, if proven effective, could have direct impact on clinical practice and help selected patients with hypertension lead better quality of life and have better health outcomes,” said Assoc Prof Calvin Chin.