AI-Enabled Chest X-ray for Cardiothoracic Ratio from Qure.ai Receives FDA Clearance
Images
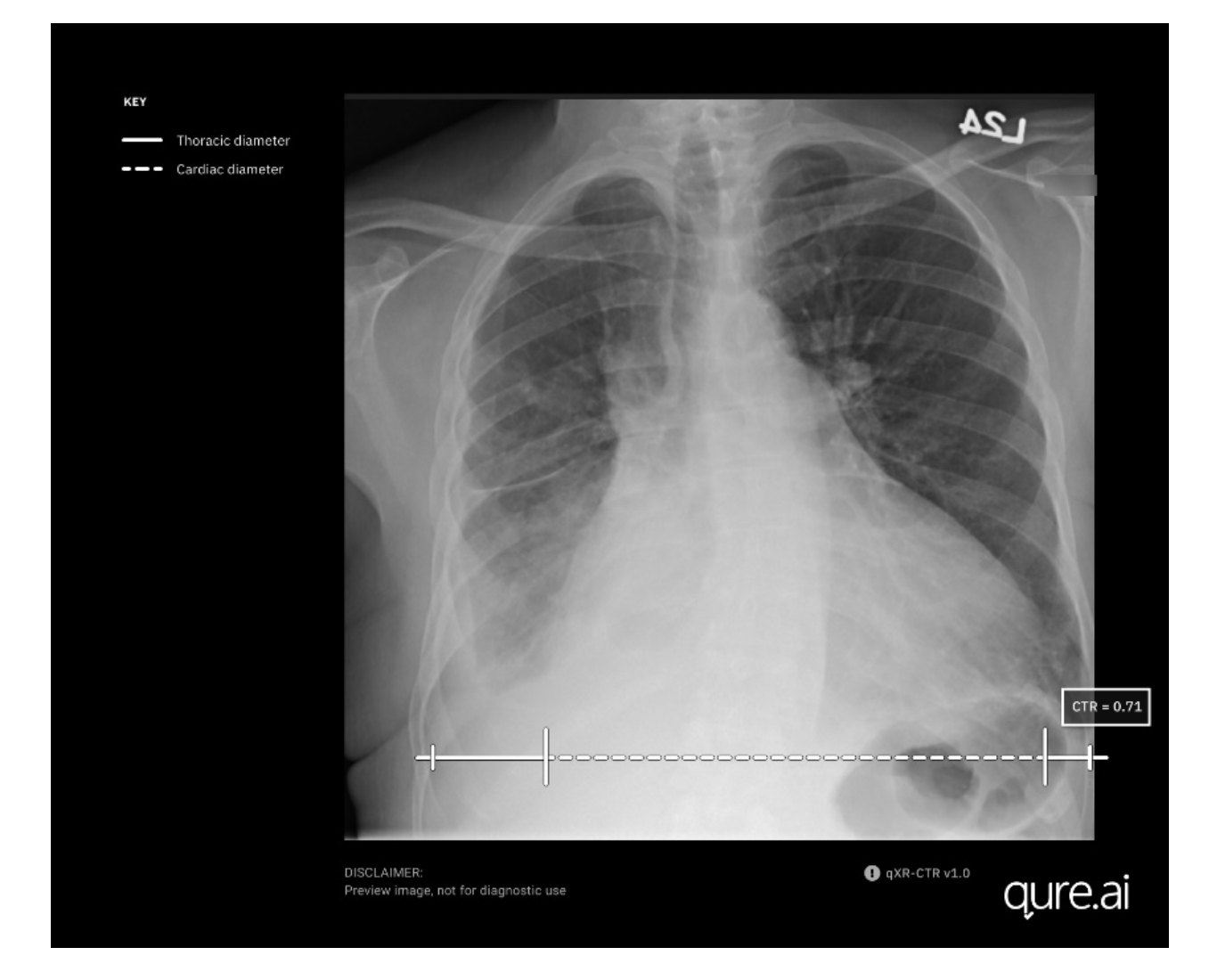
The US FDA has cleared qXR-CTR, Qure.ai’s artificial intelligence-enabled chest X-ray solution for use in measuring the cardiothoracic ratio (CTR).
The qXR-CTR is a deep-learning-based computer vision algorithm designed for use by physicians in all inpatient and outpatient settings, to automate the CTR assessment on chest radiographs (CXR). It precisely measures the ratio of the maximum transverse diameter of the heart to the maximum inner transverse diameter of the thoracic cavity, providing the most accurate indicator of cardiomegaly on plain film. This cutting-edge technology leverages artificial intelligence algorithms to deliver precise and efficient results, saving time for physicians and improving diagnostic accuracy.
Prashant Warier, Co-Founder and CEO at Qure.ai, said, "We are delighted to receive FDA clearance for qXR-CTR. This cutting-edge algorithm enhances the accuracy and efficiency of CTR assessment and empowers healthcare professionals with a valuable tool to diagnose and monitor risk of heart failure. This achievement reaches an industry record for the greatest number of FDA-cleared findings on CXR scans, demonstrating Qure.ai's commitment to advancing better patient outcomes through AI-driven solutions."
The clearance of qXR-CTR marks the company's 12th FDA-cleared algorithm, solidifying its position as an industry leader. Previous FDA-cleared findings by Qure.ai include Endotracheal Tube location, Tracheostomy tube location, Pneumothorax, and Pleural Effusion identification for CXR; qER for intracranial haemorrhage detection on head CT scans, and qER Quant for quantifying critical abnormalities on head CT scans.
With qXR-CTR now being cleared by the FDA, Qure's chest X-ray algorithm can be deployed to jointly screen for increased cardiothoracic ratio (CTR) and Pleural effusion along with other radiographic markers associated with the presence of heart failure. This remarkable achievement is a significant advancement for medical imaging and cardiac care, opening new avenues for the early detection of heart failure through automated assessment of chest radiographs.
"Integrating AI into cardiac diagnostics has long shown immense promise, and Qure.ai’s latest advancement with qXR-CTR is a testament to how much of that potential is now being realized. Early detection of heart failure is a challenge, but with tools like these, we are narrowing the gap. The combination of identifying increased cardiothoracic ratio and pleural effusion, in particular, is a significant stride. I believe this amplifies the crucial role AI-driven
solutions play in supporting cardiologists and enhancing patient outcomes. I look forward to seeing how technologies such as this one will further evolve the landscape of cardiac care,” says Tariq Ahmad, Chief, MD, MPH, Heart Failure Program - Section of Cardiology, Yale School of Medicine.
Related Articles
Citation
AI-Enabled Chest X-ray for Cardiothoracic Ratio from Qure.ai Receives FDA Clearance. Appl Radiol.
October 9, 2023